A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
EDUCART PUBLICATION-SAMPLE PAPER 5-SECTION - B
- What is the dipole moment of a dipole consisting two equal and opposit...
Text Solution
|
- What is inherent characteristic of matter:
Text Solution
|
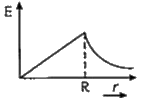
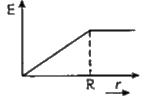
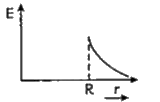
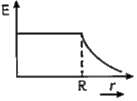
- vec (E) due to uniformly charged sphere of radius R as a function of d...
Text Solution
|
- Electric field at a point is:
Text Solution
|
- Condition for step-down transformer is:
Text Solution
|
- The flux through the surface:
Text Solution
|
- Effective capacitance of (10)/(11) is required to obtain from such cap...
Text Solution
|
- Two plates, one at 300 V, other at - 100 V are 4 cm apart. The voltage...
Text Solution
|
- The circuit has total resistance of:
Text Solution
|
- If a bar magnet is cut in half, then new magnetic moment m and pole st...
Text Solution
|
- Value of earth's magnetic field inside a metallic cage is:
Text Solution
|
- Relation between earth's magnetic field is given by:
Text Solution
|
- Due to orbital motion, magnetic moment is:
Text Solution
|
- At a point on the right bisector of a magnetic dipole the magnetic pot...
Text Solution
|
- At a certain B(H) = (1)/(sqrt(3)) B dip, angle is:
Text Solution
|
- The condition of minimum impedance is:
Text Solution
|
- The natural frequency of given circuit is shown by:
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A): Current should not be passed through potentiometer for ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A): Resistivity of a conductor, increases on increasing tem...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A): As the relaxation time Increases drift velocity increas...
Text Solution
|