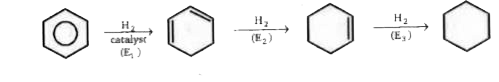
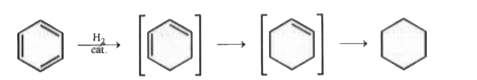
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise LEVEL - 2|95 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise LEVEL - 2 (SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS )|13 VideosCARBOXYLIC ACID AND THEIR DERIVATIVES
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise LEVEL-2( SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS)|1 VideosGRIGNARD REAGENT
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise Level-2 (Subjective Problems)|6 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MS CHOUHAN-GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY -LEVEL - 2 (SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS )
- (E = activation energy) Relation between activation energies of abo...
Text Solution
|
- How many 2^@ carbon in the following ?
Text Solution
|
- Find out the double bond equivalent (DBE) value of the given following...
Text Solution
|
- Total number of functional groups present in the given following compo...
Text Solution
|
- Total number of a-hydrogen in the given following compound is:
Text Solution
|
- How many carbon atom present in the parent chain in the given followin...
Text Solution
|
- Total number of DBE value in :
Text Solution
|
- How many isomers of C(4)H(10)O reacts with Na metal to evolve H2 gas...
Text Solution
|
- Match the following columns
Text Solution
|
- Which of the given following compound will react with NaHCO3 or solubl...
Text Solution
|
- How many compound are stable after deprotonation ?
Text Solution
|
- Sum of types of functional group and DBE value for given compound is X...
Text Solution
|
- P = Number of anti-aromatic compound, so the value of x is : Q =...
Text Solution
|
- X = number of(+M) group attached with phenyl ring, so the value of x i...
Text Solution
|