A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise LEVEL - 2 (SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS )|13 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise LEVEL - 2 (SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS )|13 VideosCARBOXYLIC ACID AND THEIR DERIVATIVES
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise LEVEL-2( SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS)|1 VideosGRIGNARD REAGENT
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise Level-2 (Subjective Problems)|6 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MS CHOUHAN-GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY -LEVEL - 2
- Match the column (I) and (II).
Text Solution
|
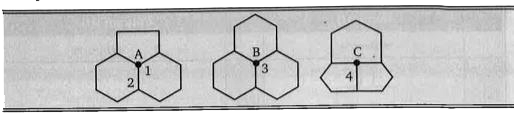
- The junctions centered on atoms A, B and C on the given structure. ...
Text Solution
|
- The junctures centred on atoms A, B and C on the given structure. ...
Text Solution
|
- Select the most stable structure in each of the following
Text Solution
|
- Select the most stable structure in each of the following
Text Solution
|
- Select the most stable structure in each of the following
Text Solution
|
- Match the column I and II. (Matrix)
Text Solution
|
- Match the column I and II. (Matrix)
Text Solution
|
- Identify the most stable structure in each of the following:
Text Solution
|
- Identify the most basic compound in the following.
Text Solution
|
- Identify the most acidic hydrogen containing compound from the followi...
Text Solution
|
- Give the type of hybridization present at each atom. (i) C1 - ……...
Text Solution
|
- Predict the direction of the following equilibrium. Write your answer ...
Text Solution
|
- Match the column I and II. (Matrix)
Text Solution
|
- Match the column I and II.
Text Solution
|
- Match the column I and II.
Text Solution
|
- Sum of molecular mass of gas (A + C) is :
Text Solution
|
- Ph-overset(O)overset(||)C-O-Hoverset(NaHCO3)rarr(A) gas Ph - C-=CHo...
Text Solution
|
- Match the column I and II.
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following reaction of boron trifluoride (BF3) and aceton...
Text Solution
|