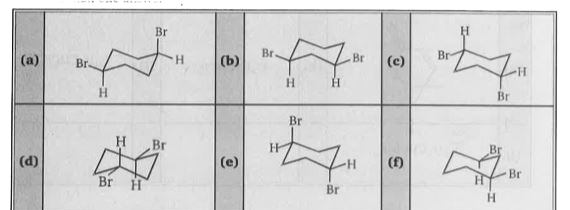
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ISOMERISM (STRUCTURAL & STEREOISOMERISM)
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise LEVEL 2 (SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS)|17 VideosISOMERISM (STRUCTURAL & STEREOISOMERISM)
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise LEVEL 2 (SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS)|17 VideosHYDROCARBONS (ALKYNES)
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise Level -1|32 VideosIUPAC NAME
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise LEVEL-2 (SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS ) |1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MS CHOUHAN-ISOMERISM (STRUCTURAL & STEREOISOMERISM)-LEVEL 2
- Examine the following formulas and select those pairs that satisfy the...
Text Solution
|
- Examine the following formulas and select those pairs that satisfy the...
Text Solution
|
- Examine the following formulas and select those pairs that satisfy the...
Text Solution
|
- Examine the following formulas and select those pairs that satisfy the...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following statements regarding the given projection (True...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following statements regarding the given projection (True...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following statements regarding the given projection (True...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following statements regarding the given projection (True...
Text Solution
|
- Examine the following structural formulas and select those that are ch...
Text Solution
|
- The configuration of eight compounds, a through h are shown below, usi...
Text Solution
|
- The configuration of eight compounds, a through h are shown below, usi...
Text Solution
|
- The configuration of eight compounds, a through h are shown below, usi...
Text Solution
|
- The configuration of eight compounds, a through h are shown below, usi...
Text Solution
|
- The structural formula of ten compounds, (I) through (X) are drawn bel...
Text Solution
|
- The structure of one of the enantiomers of the amino acid cysteine is ...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the following double bonds either E, Z or None (N) in the com...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Bongkrekic acid is a toxic compound produced by Pseudomonas cocove...
Text Solution
|
- Designate the following double bonds as E, Z or none (N) configuration...
Text Solution
|
- The following compounds may exist as two or more stereoisomers. These ...
Text Solution
|
- Find relationship between given pair :
Text Solution
|