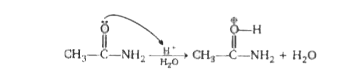
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CARBOXYLIC ACID AND THEIR DERIVATIVES
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise LEVEL-2|1 VideosCARBOXYLIC ACID AND THEIR DERIVATIVES
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise LEVEL-2( SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS)|1 VideosCARBENE AND NITRENE
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise LEVEL-2 |5 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise LEVEL - 2 (SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS )|13 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems