A dye, phenolphtnalein is prepared by reacting phenol with phthalic anhydride in acidic medium. It give pink colour in alkaline medium due to extended conjugation I a new complex formed (phthalein- dye test) identify the compled A:

A dye, phenolphtnalein is prepared by reacting phenol with phthalic anhydride in acidic medium. It give pink colour in alkaline medium due to extended conjugation I a new complex formed (phthalein- dye test) identify the compled A:


A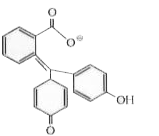

B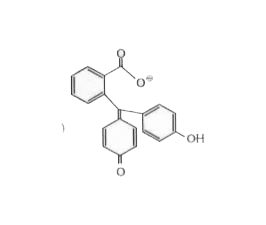

C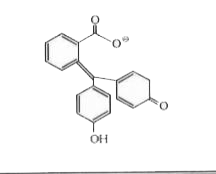

D
None
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
B
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Yellow dye can be prepared by a coupling reaction of benzene diamonium chloride in acid medium with X. Identify X from the following .
All titration which involves the direct titration of Iodine with a reducing agent are grouped under lodimetry. Iodimetry is employed to determine the strength of reducing agent such as sodium thio sulphate I_(2) + 2Na_(2)S_(2)O_(3) rarr 2I^(-)+S_(4)O_(6)^(-) If iodine is liberated as a result of chemical reaction involving oxidation of an idodide ion by a strong oxidizing agent in neutral or acidic medium the liberated iodine is then titrated with reducing agent. This titration is called lodometry. Todometry is used to estimate the strength of oxidizing agent. For example the estimation of Cu^(++) with thiosulphate. Cu^(+ +) +I^(-) Cu_(2)I_(2)+I_(2) , I_(2) +S_(2)O_(3)^(-) rarrS_(4)O_(6)^(-) +I^(-) Starch used as indicator near the end point which form blue colour complex with I_(3)^(-) . The blue colour disappears when When 159.50g of CuSO_4 in a solution is reacted with KI, then the liberated iodine required 100 ml 1 M Na_(2)S_(2)O_3 for complete reaction, then what is the percentage purity of sample used in making the solution.
All titration which involves the direct titration of Iodine with a reducing agent are grouped under lodimetry. Iodimetry is employed to determine the strength of reducing agent such as sodium thio sulphate I_(2) + 2Na_(2)S_(2)O_(3) rarr 2I^(-)+S_(4)O_(6)^(-) If iodine is liberated as a result of chemical reaction involving oxidation of an idodide ion by a strong oxidizing agent in neutral or acidic medium the liberated iodine is then titrated with reducing agent. This titration is called lodometry. Todometry is used to estimate the strength of oxidizing agent. For example the estimation of Cu^(++) with thiosulphate. Cu^(+ +) +I^(-) Cu_(2)I_(2)+I_(2) , I_(2) +S_(2)O_(3)^(-) rarrS_(4)O_(6)^(-) +I^(-) Starch used as indicator near the end point which form blue colour complex with I_(3)^(-) . The blue colour disappears when In the reaction, 2CuSO_(4) +4KI rarr Cu_(2)I_(2) + 2K_(2)SO_(4)+I_2 the ratio of equivalent weight of CuSO_4 to its molecular weight is:
All titration which involves the direct titration of Iodine with a reducing agent are grouped under lodimetry. Iodimetry is employed to determine the strength of reducing agent such as sodium thio sulphate I_(2) + 2Na_(2)S_(2)O_(3) rarr 2I^(-)+S_(4)O_(6)^(-) If iodine is liberated as a result of chemical reaction involving oxidation of an idodide ion by a strong oxidizing agent in neutral or acidic medium the liberated iodine is then titrated with reducing agent. This titration is called lodometry. Todometry is used to estimate the strength of oxidizing agent. For example the estimation of Cu^(++) with thiosulphate. Cu^(+ +) +I^(-) Cu_(2)I_(2)+I_(2) , I_(2) +S_(2)O_(3)^(-) rarrS_(4)O_(6)^(-) +I^(-) Starch used as indicator near the end point which form blue colour complex with I_(3)^(-) . The blue colour disappears when 10 mL of H_2O_2 solution on treatment with KI and titration of liberated I_2 required 10 mL of 1 N hypo . Thus H_2O_2 is :
K_2Cr_2O_7 acts as a good oxidizing agent in acidic medium underset("Orange")(Cr_(2)O_(7)^(2-)) + 14H^(+) + 6e^(-) rarr underset("Green")(2Cr^(3+)) + 7H_2O In alkaline solution, orange colour of Cr_(2)O_(7)^(2-) chages to yellow colour due to formation of Cr_2O_(4)^(2-) and again yellow colour changes to orange colour on changing the solution to acidic medium underset("Orange")(Cr_2O_7^(2-))+2OH^(_) rarrunderset("Yellow")(Cr_2O_7^(2-))+H_2O underset("Yellow")(2CrO_(4)^(2_-)) + 2H^(+) rarr underset("Orange")(Cr_(2)O_(7)^(2-) + H_(2)O) Cr_(4)^(2-) and Cr_(2)O_(7)^(2-) exist in equilibrium at pH =4 and are interconvertible by altering the pH of the solution. When heated with H_2SO_4 and metal chloride K_2Cr_2O_7 gives vapour of chromyl chloride (CrO_2Cl_2) . Chromyl chloride (CrO_2Cl_2) when passed into aqueous NaOH solution, yellow colour solution of CrO_(4)^(2-) is obtained. This on reaction with lead acetate gives yellow ppt. PbCrO_4 . When H_2O_2 is added to an acidified solution of dichromate ion, a complicated reaction occurs. The products obtained depend on the pH and concentration of dichromate. Cr_2O_7^(2-)+2H^(+) + 4H_(2)O_(2) rarr 2Cr(O_2)+5H_2O A deep blue-violet coloured peroxo compound, CrO(O_2)_2, ' called chromic peroxide is formed. This decomposes rapidly in aqueous solution into Cr^(3+) and xygen. What happens when a solution of potassium chromate is treated with an excess of dilute nitric acid?
K_2Cr_2O_7 acts as a good oxidizing agent in acidic medium underset("Orange")(Cr_(2)O_(7)^(2-)) + 14H^(+) + 6e^(-) rarr underset("Green")(2Cr^(3+)) + 7H_2O In alkaline solution, orange colour of Cr_(2)O_(7)^(2-) chages to yellow colour due to formation of Cr_2O_(4)^(2-) and again yellow colour changes to orange colour on changing the solution to acidic medium underset("Orange")(Cr_2O_7^(2-))+2OH^(_) rarrunderset("Yellow")(Cr_2O_7^(2-))+H_2O underset("Yellow")(2CrO_(4)^(2_-)) + 2H^(+) rarr underset("Orange")(Cr_(2)O_(7)^(2-) + H_(2)O) Cr_(4)^(2-) and Cr_(2)O_(7)^(2-) exist in equilibrium at pH =4 and are interconvertible by altering the pH of the solution. When heated with H_2SO_4 and metal chloride K_2Cr_2O_7 gives vapour of chromyl chloride (CrO_2Cl_2) . Chromyl chloride (CrO_2Cl_2) when passed into aqueous NaOH solution, yellow colour solution of CrO_(4)^(2-) is obtained. This on reaction with lead acetate gives yellow ppt. PbCrO_4 . When H_2O_2 is added to an acidified solution of dichromate ion, a complicated reaction occurs. The products obtained depend on the pH and concentration of dichromate. Cr_2O_7^(2-)+2H^(+) + 4H_(2)O_(2) rarr 2Cr(O_2)+5H_2O A deep blue-violet coloured peroxo compound, CrO(O_2)_2, ' called chromic peroxide is formed. This decomposes rapidly in aqueous solution into Cr^(3+) and xygen. CrO_3 on reaction with HCl and the product on reaction with NaOH(aq) give respectively
K_2Cr_2O_7 acts as a good oxidizing agent in acidic medium underset("Orange")(Cr_(2)O_(7)^(2-)) + 14H^(+) + 6e^(-) rarr underset("Green")(2Cr^(3+)) + 7H_2O In alkaline solution, orange colour of Cr_(2)O_(7)^(2-) chages to yellow colour due to formation of Cr_2O_(4)^(2-) and again yellow colour changes to orange colour on changing the solution to acidic medium underset("Orange")(Cr_2O_7^(2-))+2OH^(_) rarrunderset("Yellow")(Cr_2O_7^(2-))+H_2O underset("Yellow")(2CrO_(4)^(2_-)) + 2H^(+) rarr underset("Orange")(Cr_(2)O_(7)^(2-) + H_(2)O) Cr_(4)^(2-) and Cr_(2)O_(7)^(2-) exist in equilibrium at pH =4 and are interconvertible by altering the pH of the solution. When heated with H_2SO_4 and metal chloride K_2Cr_2O_7 gives vapour of chromyl chloride (CrO_2Cl_2) . Chromyl chloride (CrO_2Cl_2) when passed into aqueous NaOH solution, yellow colour solution of CrO_(4)^(2-) is obtained. This on reaction with lead acetate gives yellow ppt. PbCrO_4 . When H_2O_2 is added to an acidified solution of dichromate ion, a complicated reaction occurs. The products obtained depend on the pH and concentration of dichromate. Cr_2O_7^(2-)+2H^(+) + 4H_(2)O_(2) rarr 2Cr(O_2)+5H_2O A deep blue-violet coloured peroxo compound, CrO(O_2)_2, ' called chromic peroxide is formed. This decomposes rapidly in aqueous solution into Cr^(3+) and xygen. Which of the following statements is wrong when a mixture of NaCI and K_2Cr_2O_2 is gently walmed with conc. H_2SO_4 ?
Emulsions are normally prepared by shaking the two components together vigorously although some kind of emulsifying agent usually has to added to stabilize the product. This emulsifying agent may be a soap or other surfactant (surface active) species or a lyophilic sol. Emulsions are broadly classified into two types : (i) Oil in water emulsions (O/W): Oil acts as dispersed phase and water acts as dispersion medium (ii) Water in oil emulsions (W/O) : Water acts as dispersed phase and oil acts as dispersion medium. Dye test, dilution test may be employed for identification of emulsions. Select correct statement :
Emulsions are normally prepared by shaking the two components together vigorously although some kind of emulsifying agent usually has to added to stabilize the product. This emulsifying agent may be a soap or other surfactant (surface active) species or a lyophilic sol. Emulsions are broadly classified into two types : (i) Oil in water emulsions (O/W): Oil acts as dispersed phase and water acts as dispersion medium (ii) Water in oil emulsions (W/O) : Water acts as dispersed phase and oil acts as dispersion medium. Dye test, dilution test may be employed for identification of emulsions. Read the two statements : A) Milk is an example of oil in water (O/W) type emulsion B) Cold cream is an example of water in oil (W/O) type emulsion
MS CHOUHAN-PRACTICAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-LEVEL -2
- A dye, phenolphtnalein is prepared by reacting phenol with phthalic an...
Text Solution
|
- Which isomer gives positive iodoform test?
Text Solution
|
- Which isomer gives +ive Tollen's test, also reacts with FeCl(3)?
Text Solution
|
- Which isomer reacts with NaHCO(3)?
Text Solution
|
- Which isomer on hydrolysis gives 1,4-di hydroxybenzene?
Text Solution
|
- Ph-overset(O)overset(||)(C)-OHoverset(NaHCO(3))(to)(A)"gas" Ph-OHove...
Text Solution
|