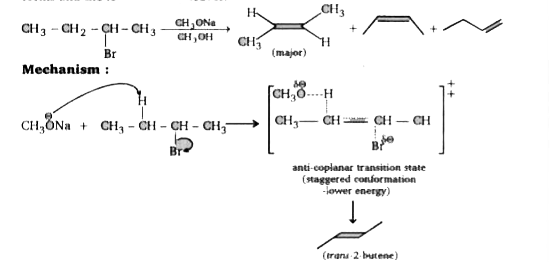
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MS CHOUHAN-ALKYL HALIDES (ELIMINATION REACTION) -LEVEL-2
- Comprehension E2 raction rarr Elimination bimolecular In the gene...
Text Solution
|
- Comprehension E2 raction rarr Elimination bimolecular In the gene...
Text Solution
|
- Comprehension E2 raction rarr Elimination bimolecular In the gene...
Text Solution
|
- Match the column :
Text Solution
|
- Match the column : HEM = Hoffmann exhaustive methylation followed ...
Text Solution
|
- Match the column :
Text Solution
|
- Match the column :
Text Solution
|
- Match the column :
Text Solution
|
- Match the column :
Text Solution
|
- Match the column :
Text Solution
|
- Sum of X + Y + Z + P =
Text Solution
|
- The correct match is
Text Solution
|
Text Solution
|
- Sum of alpha hydrogen is (A + B + C = )
Text Solution
|
- Sum of alpha -hydrogen (A + B +C)=
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following reaction
Text Solution
|
- Match the column (I) and (II)
Text Solution
|
- Match the column (I) and (II)
Text Solution
|
- Select whether the following reaent combination will result in elimina...
Text Solution
|
- Match the column (I) and (II)
Text Solution
|