A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MS CHOUHAN-ALDEHYDES AND KETONES-LEVEL-2
- Select the best choice for example (A to L) from the examples (a to n)...
Text Solution
|
- The following questions refer to the compounds (A to G) shown below :
Text Solution
|
- Match of the column :
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following table.
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following reactions and answer A and B. Suggest a re...
Text Solution
|
- Yield of each step as actually carried out in the laboratory is given ...
Text Solution
|
- Degree of unsaturation present in compound (A + B + C) is ?
Text Solution
|
- Within each set, which compound should be more reactive toward carbony...
Text Solution
|
- Match the Column (I) and Column (II). (Matrix)
Text Solution
|
- Consider reactions A through F. Those carbon atoms undergoing change, ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the possible formation of an aldehyde or ketone product when ...
Text Solution
|
- Wittig reaction : The reaction of a phosphorus ylide with an aldehyd...
Text Solution
|
- Wittig reaction : The reaction of a phosphorus ylide with an aldehyd...
Text Solution
|
- Wittig reaction : The reaction of a phosphorus ylide with an aldehyd...
Text Solution
|
- Wittig reaction : The reaction of a phosphorus ylide with an aldehyd...
Text Solution
|
- Wittig reaction : The reaction of a phosphorus ylide with an aldehyd...
Text Solution
|
- Wittig reaction : The reaction of a phosphorus ylide with an aldehyd...
Text Solution
|
- Match the column :
Text Solution
|
- Reactant (A) is :
Text Solution
|
- Product (B) is :
Text Solution
|
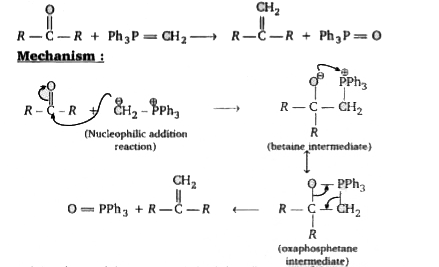
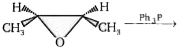 , Major product (A) is
, Major product (A) is