A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CBSE MODEL PAPER-PRACTICE PAPER 2022-Multiple Choice Questions
- Which of the following occurs during oxygen shortage in muscle cells?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following plays the important role of creating a suction ...
Text Solution
|
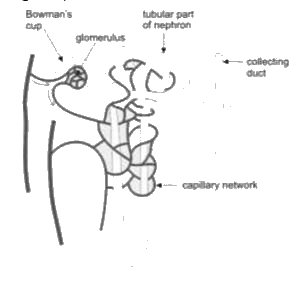
- Observe the image of a single nephron. The amount of liquid passi...
Text Solution
|
- During transpiration, water is lost in the form of water vapour throug...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following characteristics of a spherical mirror is given ...
Text Solution
|
- In the diagram shown below, a light ray is incident on a convex mirror...
Text Solution
|
- As a ray of light entered medium P from medium Q, its velocity increas...
Text Solution
|
- In the diagram shown below, a beam of light is travelling from inside ...
Text Solution
|
- The image below depicts light being split by a prism into different co...
Text Solution
|
- An object was placed at the centre of curvature of a concave lens. The...
Text Solution
|
- The Sun appears red during sunset because
Text Solution
|
- The path of light rays passing through a glass prism is BEST represent...
Text Solution
|
- w SnO(2) + x H(2) to y Sn + z H(2) O For which of the following valu...
Text Solution
|
- A solution of an acid with pH 5.1 is given. Which of the following can...
Text Solution
|
- Aditi adds dropwise 25 ml of concentrated HCl to 25 ml of concentrated...
Text Solution
|
- Anand took four colourless solutions P, Q, R and S, and performed the ...
Text Solution
|
- Some activities cause the soil and water resources in that area to bec...
Text Solution
|
- Shown below is a container that is used in the transportation of goods...
Text Solution
|
- Payal has to arrange the following in DECREASING order of hydroxide io...
Text Solution
|
- A piece of zinc (Zn) - a reactive metal - was dropped into a test tube...
Text Solution
|