To determine in which of the given circuits the bulb will glow, we need to analyze each circuit option step by step.
### Step-by-Step Solution:
1. **Understanding Circuit Components**:
- A circuit typically consists of a power source (like a battery or cell), a load (like a bulb), and connecting wires. For the bulb to glow, the circuit must be complete, allowing electric current to flow.
2. **Analyzing Option 1**:
- In this circuit, the wires are connected to the cell, but both ends of the wires are connected to the same terminal of the cell.
- **Conclusion**: This creates an incomplete circuit. Since the circuit is incomplete, **no electric current flows**, and therefore, **the bulb will not glow**.
3. **Analyzing Option 2**:
- This circuit has a cell connected to a bulb, but there is a string (which is a non-conductor) connected in the circuit.
- **Conclusion**: The presence of the non-conductor means that **the electric current cannot flow** through this circuit. Thus, **the bulb will not glow**.
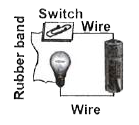
4. **Analyzing Option 3**:
- In this circuit, there is a cell, a bulb, a switch, and a rubber band (which is also a non-conductor).
- The wires connect the cell to the bulb, but the rubber band interrupts the circuit.
- **Conclusion**: Since the rubber band is a non-conductor, **the current cannot flow** through this circuit either. Therefore, **the bulb will not glow**.
5. **Final Analysis**:
- After analyzing all three options, we find that in none of the circuits does the bulb glow because all circuits are either incomplete or contain non-conductors that prevent current flow.
### Summary:
- **Option 1**: Incomplete circuit - Bulb does not glow.
- **Option 2**: Non-conductor present - Bulb does not glow.
- **Option 3**: Non-conductor present - Bulb does not glow.
**Final Answer**: The bulb will not glow in any of the given circuits.