A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
SCIENCE OLYMPIAD FOUNDATION -WORK AND ENERGY-ACHIEVERS SECTION (HOTS)
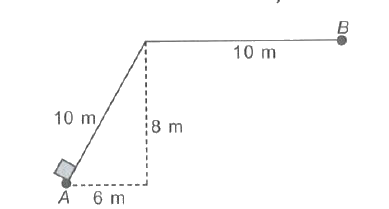
- A box of 5 kg mass moves up a ramp from point A to point B at a const...
Text Solution
|
- A mass of M kg is suspended by a weightless string. The horizontal for...
Text Solution
|
- A body moves under a variable force. For the body a plot of velocity ...
Text Solution
|
- Two inclined frictionless tracks, one gradual and the other steep mee...
Text Solution
|
- The diagram shows a cyclist moving down a small hill at P before trav...
Text Solution
|
- The diagram shows an object released from point X and travelling on a ...
Text Solution
|