A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
SCIENCE OLYMPIAD FOUNDATION -FUN WITH MAGNETS -ACHIEVERS SECTION (HOTS)
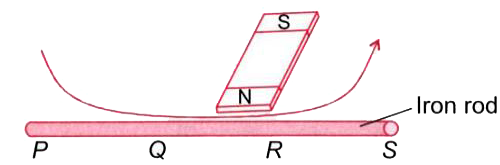
- Ashwini magnetised a piece of iron rod using the stroking method as sh...
Text Solution
|
- Arun suspended a bar magnet on a string as shown in the diagram. He br...
Text Solution
|
- When Asha suspended four bars of different materials from a pole and b...
Text Solution
|
- Arpita is standing in the middle of a cross road with a compass. The r...
Text Solution
|
- A plotting compass is moved slowly towards the metal bar X along the p...
Text Solution
|
- Observe the given figure and identify the correct statements. (i...
Text Solution
|