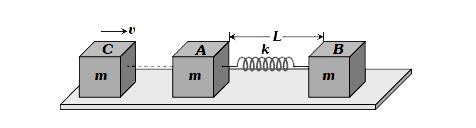
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
WORK, ENERGY POWER AND COLLISION
ERRORLESS|Exercise NCERT BASED QUESTIONS (Power)|18 VideosWORK, ENERGY POWER AND COLLISION
ERRORLESS|Exercise NCERT BASED QUESTIONS (Elastic and Inelastic Collision)|44 VideosWORK, ENERGY POWER AND COLLISION
ERRORLESS|Exercise NCERT BASED QUESTIONS (Work Done by Variable Force)|26 VideosWAVES AND SOUND
ERRORLESS|Exercise ASSERTION & REASON |25 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ERRORLESS-WORK, ENERGY POWER AND COLLISION-NCERT BASED QUESTIONS (Conservation of Energy and Momentum)
- An open knife of mass m is dropped from a height h on a wooden floor. ...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical cylindrical vessels with their bases at the same level e...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical blocks A and B , each of mass m resting on smooth floor ...
Text Solution
|
- A small body is released from a height H of an inclined plane. At the ...
Text Solution
|
- Two plates each of the mass m are connected by a massless spring as sh...
Text Solution
|
- An electron and a proton are moving under the influence of mutual forc...
Text Solution
|
- A proton is kept at rest. A positively charged particle is released fr...
Text Solution
|
- Figure below shows a small mass connected to a string, which is attach...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is acted upon by a force given by F = - alphax^(3) -betax^...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m slides from rest at a height H on a frictionless inc...
Text Solution
|
- A body moves in a circular orbit of radius R under the action of a cen...
Text Solution
|
- A particle with total mechanical energy, which is small and negative, ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform thin rod of length 2L and mass m lies on a horizontal table....
Text Solution
|
- The graph between the resistive force F acting on a body and the dista...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following graph is correct between kinetic energy E, pote...
Text Solution
|
- The potential energy of the system is represented in the first figure....
Text Solution
|
- The graph betwee sqrt(E) and (1)/(p) is (E=kinetic energy and p= momen...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 4 m which is at rest explodes into three fragments....
Text Solution
|
- A particle is dropped a height h. A constant horizontal velocity is gi...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the diagram shown in figures respresents variation of total m...
Text Solution
|