A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ERRORLESS-WORK, ENERGY POWER AND COLLISION-PAST YEARS QUESTIONS
- A bomb of mass 3.0 kg explodes in air into two pieces of masses 2.0 kg...
Text Solution
|
- A vertical spring with force constant k is fixed on a table. A ball of...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical ball of mass 20kg is stationary at the top of a hill of he...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 10 kg, moving in x-direction with a constant speed of ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass M starting from rest undergoes uniform acceleration...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass 1 kg begins to move under the action of a time depende...
Text Solution
|
- A body is moved along a straight line by a machine delivering constant...
Text Solution
|
- A partical of mass m is driven by a machine that deleveres a constant ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball hits a vertical wall horizontal at 10 m/s bounces back at 10 m/...
Text Solution
|
- A body falling from a height of 10m rebounds from hard floor. If it lo...
Text Solution
|
- A neutron makes a head-on elastic collision with a stationary deuteron...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is thrown vertically downwards from a height of 20 m with an in...
Text Solution
|
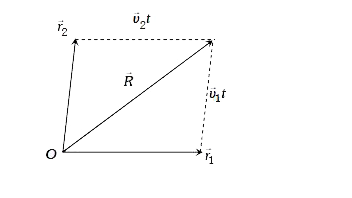
- Two particles A and B, move with constant velocities vec(v(1))" and "v...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles of masses m1,m2 move with initial velocities u1 and u2 ...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical balls A and B having velocity of 0.5 m//s and -0.3 m//s ...
Text Solution
|
- Body A of mass 4m moving with speed u collides with another body B of ...
Text Solution
|
- In an inelastic collision, what is conserved
Text Solution
|
- A metal ball of mass 2 kg moving with a velocity of 36km//h has a head...
Text Solution
|
- Water falls from a height of 60m at the rate of 15 kg/s to operate a t...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass 0.15kg is dropped from a height 10m strikes the ground ...
Text Solution
|