A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROSTATICS
ERRORLESS|Exercise NCERT BASED QUESTIONS (Capacitance)|59 VideosELECTROSTATICS
ERRORLESS|Exercise NCERT BASED QUESTIONS (Grouping of Capacitors)|58 VideosELECTROSTATICS
ERRORLESS|Exercise NCERT BASED QUESTIONS (Electric Dipole)|21 VideosELECTRONICS
ERRORLESS|Exercise Assertion & Reason|26 VideosMAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT
ERRORLESS|Exercise ASSERTION & REASON |18 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ERRORLESS-ELECTROSTATICS-NCERT BASED QUESTIONS (Electric Flux and Gauss.s Law)
- Electric field of an infinitely long straight wire is proportional to:
Text Solution
|
- Electric charge is uniformly distributed along a along straight wire o...
Text Solution
|
- q(1),q(2),q(3) and q(4) are point charges located at point as shown in...
Text Solution
|
- Gauss’s law should be invalid if
Text Solution
|
- The electric intensity due to a uniformly charged infinite cylinder of...
Text Solution
|
- The electric flux for Gaussian surface A that enclose the charge parti...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge causes an electric flux of -1.0 xx10^3 Nm^(-2)C^(-1) ...
Text Solution
|
- An infinitely long thin straight wire has uniform linear charge densit...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shown below is a distribution of charges. The flux of electric ...
Text Solution
|
- A charge 10 muC is placed at the centre of a hemisphere of radius R = ...
Text Solution
|
- The total electric flux through a cube when a charge 8q is placed at o...
Text Solution
|
- The adjacent diagram shows a charge +Q held on an insulating support S...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere of radius R has a volume density of charge rho= kr, where r i...
Text Solution
|
- The electric field in a certain region is acting radially outwards and...
Text Solution
|
- five charge q(1),q(2),q(3),q(4)and q(5) are fixed at their positions a...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a solid cube made up of insulating material having a uniform ...
Text Solution
|
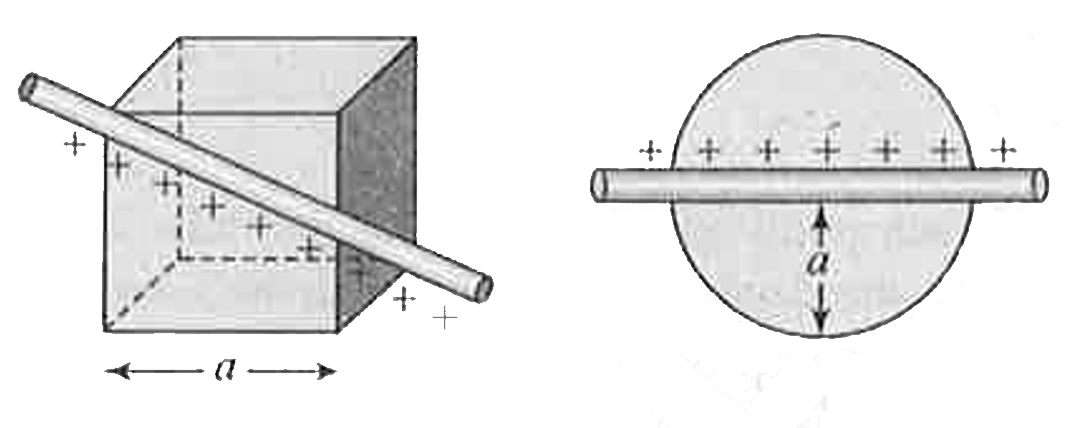
- A linear charge having linear charge density lambda pentrates a cube d...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge q is placed at one corner of a cube of edge a. The flu...
Text Solution
|
- In figure +Q charge is located at one of the edge of the cube as show...
Text Solution
|
- A charge Q is enclosed by a Gaussian spherical surface of radius R. If...
Text Solution
|