A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
KINETIC THEORY OF GASES
ERRORLESS|Exercise ASSERTION AND REASON |16 VideosKINETIC THEORY OF GASES
ERRORLESS|Exercise NCERT BASED QUESTIONS (Pressure and Energy)|31 VideosGRAVITATION
ERRORLESS|Exercise Assertion and Reason |25 VideosMOTION IN ONE DIMENSION
ERRORLESS|Exercise ASSERTION AND REASON|24 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ERRORLESS-KINETIC THEORY OF GASES -PAST YEARS QUESTIONS
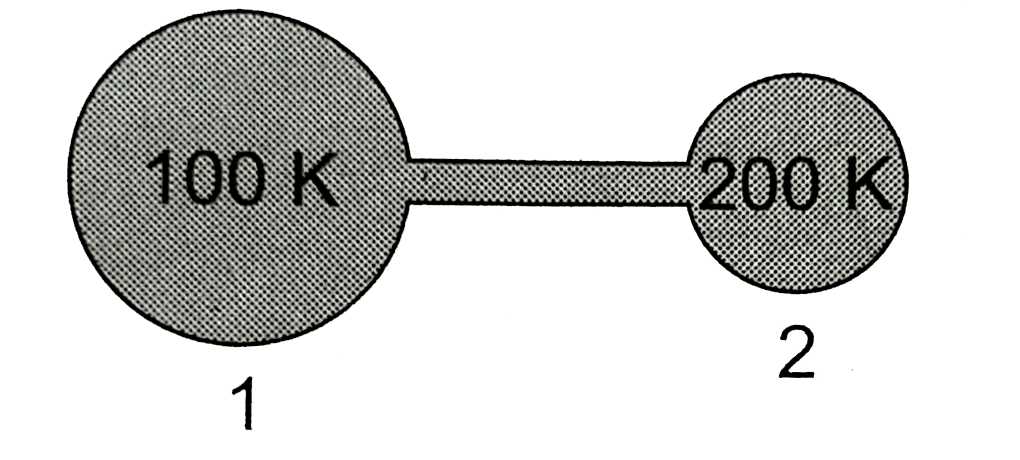
- Figure shows two flasks connected to each other. The volume of the fla...
Text Solution
|
- Two balloons are filled one with pure He gas and the other with air r...
Text Solution
|
- Two vessels separately contain two ideal gases A and B at the same tem...
Text Solution
|
- The figure below shows the plot of (PV)/(nT) versus P for oxygen gas a...
Text Solution
|
- The pressure (p) and the dencity rho of given mass of a gas expressed ...
Text Solution
|
- If pressure of CO(2) (real gas ) in a container is given by P = (RT)/...
Text Solution
|
- Th rate of diffusion is
Text Solution
|
- The molecules of a given mass of gas have a rms velocity of 200 m//sec...
Text Solution
|
- According to the kinetic theory of gases, at absolute temperature
Text Solution
|
- Gas at a pressure P(0) in contained as a vessel. If the masses of all ...
Text Solution
|
- At constant volume, temperature is increased. Then
Text Solution
|
- For gas at a temperature T the root-mean-square speed v(rms), the most...
Text Solution
|
- At what temperature will the rms speed of oxygen molecules become just...
Text Solution
|
- Increase in temperature of a gas filled in a container would lead to :
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal diatomic gas undergoes a transition from A to B a...
Text Solution
|
- The amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1 g of ...
Text Solution
|
- The molar specific heats of an ideal gas at constant pressure and volu...
Text Solution
|
- A gas mixture consists of 2 moles of oxygen and 4 moles of argon at te...
Text Solution
|
- The ratio of the specific heats C(p)/C(v)=gamma in terms of degrees of...
Text Solution
|
- When an ideal monoatomic gas is heated at constant pressure, fraction ...
Text Solution
|