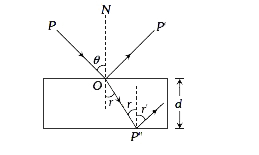
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
WAVE OPTICS AND ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY
ERRORLESS|Exercise NCERT BASED QUESTIONS (Diffraction of Light)|20 VideosWAVE OPTICS AND ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY
ERRORLESS|Exercise NCERT BASED QUESTIONS (Polarization of Light)|17 VideosWAVE OPTICS AND ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY
ERRORLESS|Exercise ASSERTION & REASON |27 VideosRAY OPTICS
ERRORLESS|Exercise Assertion & Reason|30 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ERRORLESS-WAVE OPTICS AND ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY-NCERT BASED QUESTIONS (Young’s Double Slit Experiment and Biprism)
- Two ideal slits S(1) and S(2) are at a distance d apart, and illuninat...
Text Solution
|
- Two coherent sources separated by distance d are radiating in phase ha...
Text Solution
|
- In Young's double slit experiment, the phase difference between the li...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a ray of light incident from air onto a slab of glass (refrac...
Text Solution
|
- Consider Fraunhoffer diffraction pattern obtained with a single slit i...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel monochromatic beam of light is incident normally on a narro...
Text Solution
|
- In a Young's double slit experiment (slit distance d) monochromatic li...
Text Solution
|
- n Young's double slit experiment with sodium vapour lamp of wavelength...
Text Solution
|
- In Young's double slit experiment, distance between two sources is 0.1...
Text Solution
|
- The maximum intensity of fringes in Young's experiment is I. If one of...
Text Solution
|
- The intensity of the light coming from one of the slits in a Young's d...
Text Solution
|
- In the Young's double-slit experiment,the intensity of light at a poin...
Text Solution
|
- In a Young's double slit experiment the intensity of light at each sli...
Text Solution
|
- Oil floating on water looks cloured due to interference of light. What...
Text Solution
|
- In the Young's double slit experiment , a mica slip of thickness t and...
Text Solution
|
- A thin sheet of glass (refractive index 1.5) of thickness 6 microns, i...
Text Solution
|
- When one of the slits of Young's experiment is covered with a transpar...
Text Solution
|
- A monochromatic beam of light fall on YDSE apparatus at some angle (sa...
Text Solution
|
- In a double-slit experiment, fringes are produced using light of wavel...
Text Solution
|
- In Young's double slit experiment, the aperture screen distance is 2m....
Text Solution
|