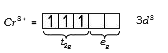
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
THE d-AND f- BLOCK ELEMENTS
ERRORLESS|Exercise Past Years Questions |55 VideosTHE d-AND f- BLOCK ELEMENTS
ERRORLESS|Exercise Assertion and Reason |11 VideosTHE d-AND f- BLOCK ELEMENTS
ERRORLESS|Exercise Assertion and Reason |11 VideosSURFACE CHEMISTRY
ERRORLESS|Exercise ASSERTION AND REASON|14 VideosTHE P -BLOCK ELEMENTS (NITROGEN, OXYGEN, HALOGEN AND NOBLE FAMILY)
ERRORLESS|Exercise ASSERTION & REASON|22 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ERRORLESS-THE d-AND f- BLOCK ELEMENTS -NCERT BASED QUESTIONS (Compounds of Transitional Elements)
- Which of the following is formed when CO(2) gas is passed through an a...
Text Solution
|
- Acidified solution of chromic acid on treatment with hydrogen peroxide...
Text Solution
|
- In aqueous solution Cr^(2+) is stronger reducing agent than Fe^(2+). T...
Text Solution
|
- The correct order of increasing oxidising power in the series is
Text Solution
|
- The correct formula of permaganic acid is
Text Solution
|
- Why Mn^(2+) compounds are more stable than Fe^(2+) compounds towards o...
Text Solution
|
- Potassium permanganate acts as an oxidant in neutral, alkaline as well...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the oxide of manganese is amohoteric
Text Solution
|
- MnO(4)^(-) reacts with Br^(-) in alkaline pH to give
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statement is incorrect for KMnO4
Text Solution
|
- Mn^(2+) can be converted into Mn^(7+) by reacting with
Text Solution
|
- Formula of thiosulphate, manganate and arsenate respectively are
Text Solution
|
- The number of moles of KMnO(4) that will be needed to react completely...
Text Solution
|
- When a brown compound of Mn (A) is teated with HCl, it gives a gas (B)...
Text Solution
|
- On addition of small amoung of KMnO(4) to concentrated H(2)SO(4), a gr...
Text Solution
|
- When KMnO(4) solution is added to oxalic acid solution , the decolouri...
Text Solution
|
- KMnO(4) acts as an oxidising agent in acidic medium. The number of mol...
Text Solution
|
- KMnO(4) acts as an oxidising agent in alkaline medium when alkaline KM...
Text Solution
|
- Why HCl not used to make the mdeium acidic in oxidation reactions of K...
Text Solution
|
- Reaction of solid KMnO4 which conc. H2SO4 produces manganese heptoxide...
Text Solution
|