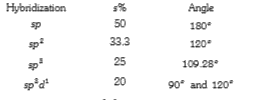A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
ERRORLESS|Exercise NCERT BASED QUESTIONS (Dipole Moment)|25 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
ERRORLESS|Exercise NCERT BASED QUESTIONS (Polarisation and Fajan.s Rule)|14 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
ERRORLESS|Exercise NCERT BASED QUESTIONS (VSEPR Theory)|46 VideosCHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
ERRORLESS|Exercise ASSERTION & REASON |12 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ERRORLESS-CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE-NCERT BASED QUESTIONS (Hybridisation)
- Which of the following pair has same structure?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is not tetrahedral ?
Text Solution
|
- As the s-character of hybridisation orbital increases, the bond angle
Text Solution
|
- The shape of IF7 molecule is
Text Solution
|
- Hybridization and shape of BrF5 is
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following is a planar molecule? (A) \(NH{3}\) (B) \...
Text Solution
|
- The percentage s-character of the hybrid orbitals in methane , ethene ...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is non-linear molecule
Text Solution
|
- Among the compounds BF(3), NCI(3), H(2)S, SF(4) and BeCI(2)., identify...
Text Solution
|
- Geometry of ammonia molcule and the hybridisation of nitrogen involve...
Text Solution
|
- The hybrid state of sulphur in SO3 molecule is
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following conversions involve change in both hybridis...
Text Solution
|
- All carbon atoms are sp^(2) hybridised in
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following pairs is isostractural (i.e having the same sha...
Text Solution
|
- State of hybridization of carbon atoms in vinyl acetylene is/are
Text Solution
|
- The hybridisations of atomic orbitals of nitrogen in NO2, NO3^(-) and ...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the least bond angle ?
Text Solution
|
- In the compound 'X', all the bond angles are exactly 109^(@)28. 'X' ma...
Text Solution
|
- Cl-P-Cl bond angles in PCl5 molecule are
Text Solution
|
- The bond angle and % of d-character in SF(6) are
Text Solution
|