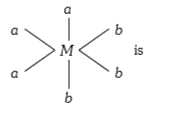
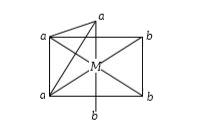
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
COORDINATION COMPOUNDS
ERRORLESS|Exercise NCERT BASED QUESTION (ISOMERISM)|1 VideosCOORDINATION COMPOUNDS
ERRORLESS|Exercise NCERT BASED QUESTION (WERNER.S COORDINATION THEORY)|16 VideosCOORDINATION COMPOUNDS
ERRORLESS|Exercise ASSERTION AND REASON|7 VideosCHEMISTRY IN EVERYDAY LIFE
ERRORLESS|Exercise Assertion & Reason|4 VideosELECTROCHEMISTRY
ERRORLESS|Exercise Assertion & Reason|11 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ERRORLESS-COORDINATION COMPOUNDS-NCERT BASED QUESTION (NOMENCLATURE, OXIDATION STATE)
- [Cr(NH(3))(6)]Cr(SCN)(6) and [Cr(NH(3))(2)(SCN)(4)][Cr(NH(3))(4)(SCN)(...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following can participate in linkage isomerism
Text Solution
|
- Octahedral complex
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compounds shows optical isomerism?
Text Solution
|
- Indicate the complex ion which shows geometrical isomerism :
Text Solution
|
- Due to the presence of ambidenate ligands coordination compounds show ...
Text Solution
|
- [Co(NH3)5Br]SO4 and [Co(NH3)5SO4]Br are the examples of:
Text Solution
|
- What kind of isomerism exists between [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3, (violet) and [Cr(...
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following will not show geometrical isomerism?
Text Solution
|
- Draw isomers of the complex ion [Co(en)(2)Cl(2)]^(+)
Text Solution
|
- The number of isomers possible for square planar complex K2[PdClBr2SCN...
Text Solution
|
- Number of possible isomers for the complex [Co(en)(2)CI(2)] will be (...
Text Solution
|
- In coordination compound [Co(en)(2)Cl(2)]Cl which is false
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following complex does not show geometrical isomerism
Text Solution
|
- Both geometrical and optical isomerism are exhibited by
Text Solution
|
- For the given complex [CoCl(2)(en)(NH(3))(2)]^(+), the number of geome...
Text Solution
|
- The complex, [Pt(py)(NH3)BrCl] will have how many geometrical isomers?
Text Solution
|
- The optically active co-ordination complex ion among the following is
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following has an optical isomer? (en=ethylenediamine) ?
Text Solution
|
- Which among the following statement are true for the complex [Co(NH(...
Text Solution
|