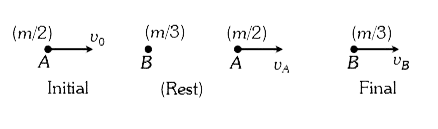A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Particle A of mass mA=m/2 moving along the x - axis with velocity v0 c...
Text Solution
|
- The de - Broglie wavelength associated with the particle of mass m mov...
Text Solution
|
- A particle A with a mass m(A) is moving with a velocity v and hits a p...
Text Solution
|
- A particle A of mass m and initial velocity v collides with a particle...
Text Solution
|
- द्रव्यमान m एवं आरम्भिक वेग upsilon के एक कण -A की टक्कर द्रव्यमान m/...
Text Solution
|
- A particle A of mass m and initial velocity v collides with a particle...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles having de-Broglie wavelengths lambda(1) and lambda(2) , ...
Text Solution
|
- Particle A of mass mA=m/2 moving along the x - axis with velocity v0 c...
Text Solution
|
- A particle A with a mass m(A) is moving a velocity v and hits a partic...
Text Solution
|