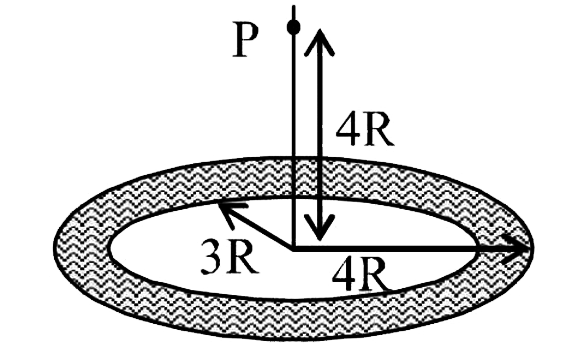
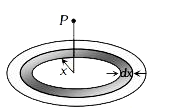
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A thin uniform disc (see figure) of mass M has outer radius 4R and in...
Text Solution
|
- A thin uniform disc (see figure) of mass M has outer radius 4R and in...
Text Solution
|
- The moment of inertia of hollow sphere (mass M) of inner radius R and ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform metal sphere of radius R and mass m is surrounded by a thin ...
Text Solution
|
- The energy required to move a body of mass m from an orbit of radius 3...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform thin rod of length 1m and mass 3kg is attached to a uniform ...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the moment of intertia of an annular disc about an axis whic...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the moment of intertia of an annular disc about an axis whic...
Text Solution
|
- M द्रव्यमान वाली एक पतली एकसमान वलयाकार डिस्क (चित्र देखिए) की बाह्य ए...
Text Solution
|