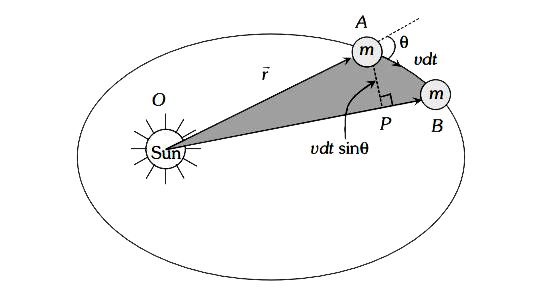
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The angular momentum of a planet of mass M moving around the sun in an...
Text Solution
|
- A planet of mass m revolves in elliptical orbit around the sun of mass...
Text Solution
|
- If 'A' is areal velocity of a planet of mass M , its angular momentum ...
Text Solution
|
- A planet of mass m is revolving round the sun (of mass M(s) in an elli...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Areal velocity of a planet around of surface area and dens...
Text Solution
|
- If the angular momentum of a planet of mass m, moving around the Sun i...
Text Solution
|
- If A is the areal velocity of a planet of mass M, its angular momentum...
Text Solution
|
- The areal velocity of the planets revolving around the sun is ………….. .
Text Solution
|
- If the angular momentum of a planet of mass m, moving around the Sun i...
Text Solution
|