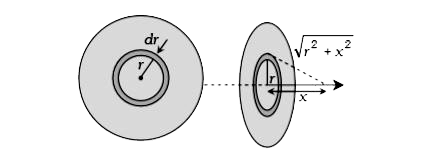
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A uniformly charged disc of radius R having surface charge density si...
Text Solution
|
- Find the electric field caused by a disc of radius a with a uniform su...
Text Solution
|
- A charge q is placed at the some distance along the axis of a uniforml...
Text Solution
|
- A uniformly charged non conducting disc with surface charge density 10...
Text Solution
|
- The surface charge density of a thin charged disc of radius R is sigma...
Text Solution
|
- The quarter disc of radius R (see figure) has a uniform surface charge...
Text Solution
|
- A flat disc of radius R charged uniformly on its surface at a surface ...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate electric field at a point on axis, which at a distance x fro...
Text Solution
|
- If sigma is surface density of charge on the charged cylinder of radiu...
Text Solution
|