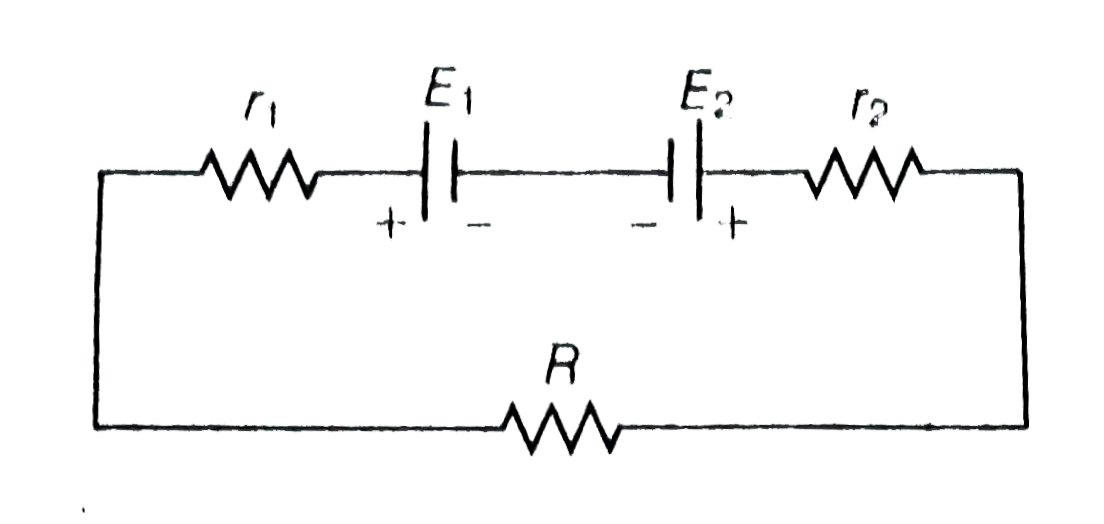
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Two cells of emf E(1) and E(2) are joined in opposition (such that E(1...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit in figure emf E(1) = 14V (internal resistance r(1) = 1O...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit in figure emf E(1) = 14V (internal resistance r(1) = 1O...
Text Solution
|
- Two resistance R(1) and R(2) are joined as shown in figure to two batt...
Text Solution
|
- Find the emf and the internal resistance of a source which is equival...
Text Solution
|
- Two batteries of E(1) internal resistance r(1) & emf E(2) internal res...
Text Solution
|
- In the cirucit (figure6.3) resistance R(1) and R(2) are known and cell...
Text Solution
|
- Two cells of emf E(1) and E(2) are joined in opposition (such that E(1...
Text Solution
|
- Two batteries of emf E(1) and E(2)(E(2) gt E(1)) and internal resistan...
Text Solution
|