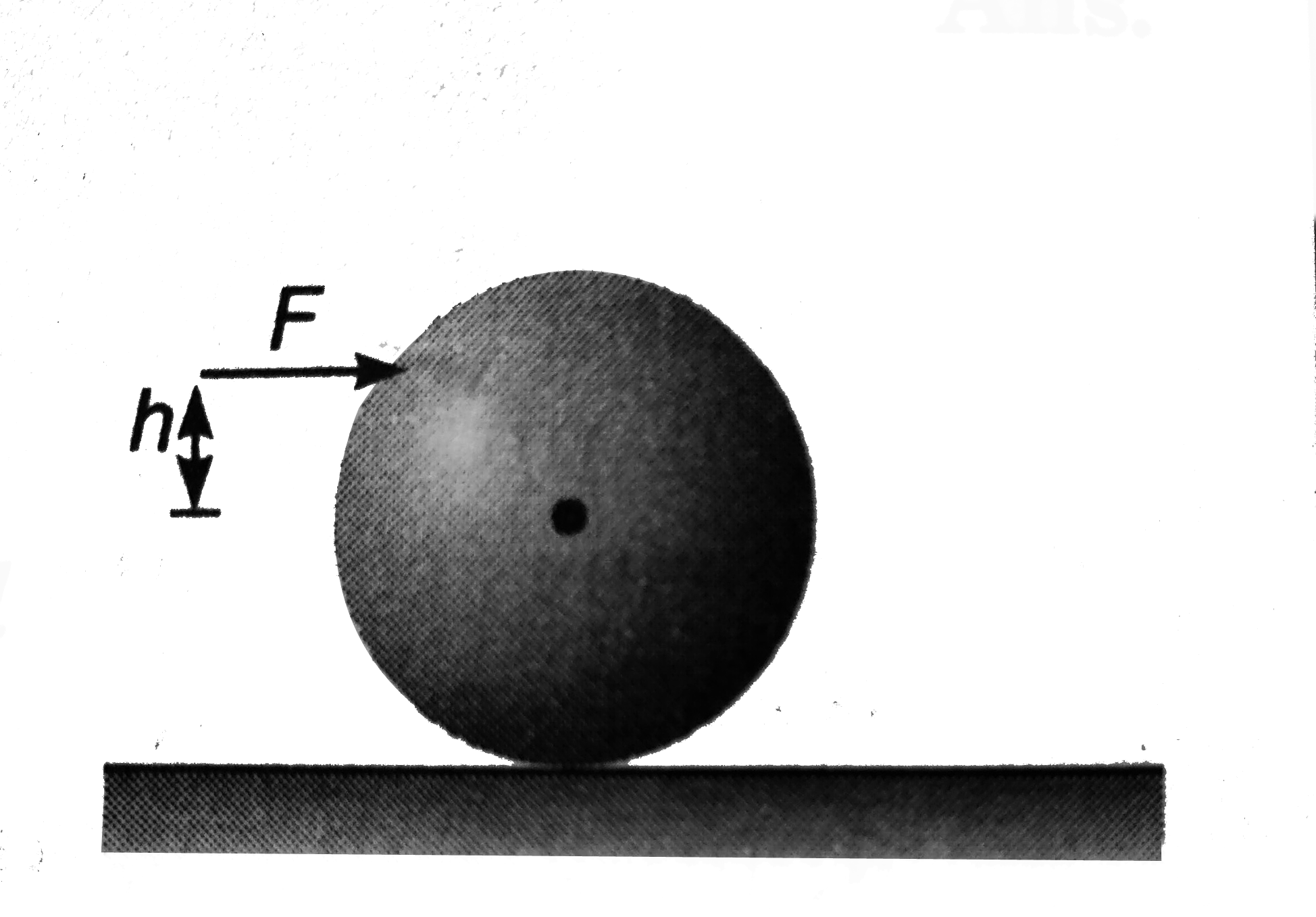
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A billiard ball, initially at rest, is given a sharp impulse by a cue....
Text Solution
|
- A solid sphere of mass M and radius R is hit by a cue at a height h ab...
Text Solution
|
- A billiard ball, initially at rest, is given a sharp impulse by a cue....
Text Solution
|
- A billiard ball of mass m and radius r, when hit in a horizontal direc...
Text Solution
|
- The cue stick hits a cue ball horizontally a distance x above the cent...
Text Solution
|
- A billiard ball is struck by a cue when it starts moving with velocity...
Text Solution
|
- A billiard ball is struck by a cue. The line of action of the applied ...
Text Solution
|
- Where must the cue hit a billiard ball so that it rolls without slidin...
Text Solution
|
- A pool cue striking a stationary billiard ball (mass=0.25kg) gives the...
Text Solution
|