Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
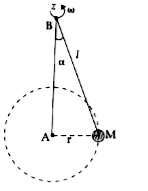
- A mass M hangs on a massless rod of length l which rotates at a consta...
Text Solution
|
- Find the angular momentum about the axis of rotation and kinetic energ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of mass m and length L is fixed to an axis, making an an...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of mass m and length l is rotating about a fixed point in the ce...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of mass m and length l is rotating about a fixed point in the ce...
Text Solution
|
- A satellite of mass m is circulating around the earth with constant an...
Text Solution
|
- A thin circular ring of mass M and radius R is rotating about its axis...
Text Solution
|
- A mass is whirled in a circular path with a constant angular velocity ...
Text Solution
|
- A satellite of mass m is circulating around the earth with constant an...
Text Solution
|