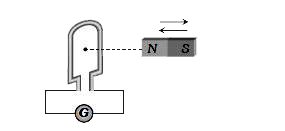
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- When a magnet is pushed in and out of a circular coil C connected to a...
Text Solution
|
- When a magnet is pushed in and out of a circular coil C connected to a...
Text Solution
|
- A magnet NS is suspended from a spring and while it oscillates, the ma...
Text Solution
|
- The diagram below shows two coils A and B placed parallel to each othe...
Text Solution
|
- A magnet N-S is suspended from a spring and while at oscillates, the m...
Text Solution
|
- The diagram below shows two coils A and B placed parallel to each othe...
Text Solution
|
- A magnet N-S is suspened from a spring and when it oscillates, the mag...
Text Solution
|
- The senstivity of a moving coil galvanometer is 'S'. If a shunt of (1/...
Text Solution
|
- What is a magnet ?
Text Solution
|