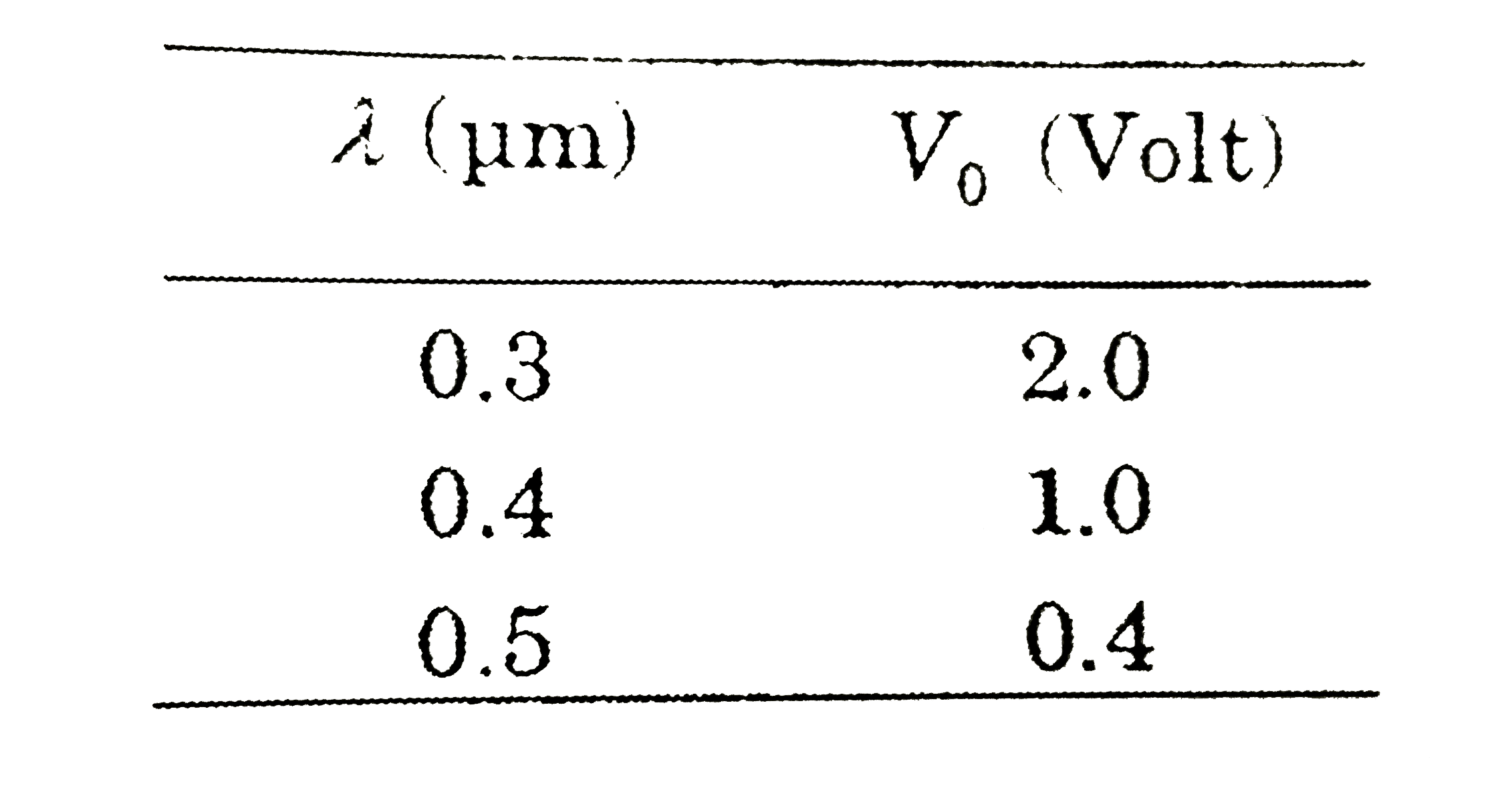A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- In a historical experiment to determine Planck's constant, a metal sur...
Text Solution
|
- a. A stopping potential of 0.82V is required to stop the emission of p...
Text Solution
|
- When light of wavelength 400nm is incident on the cathode of photocell...
Text Solution
|
- Photons of frequencies 2.2xx10^(15) Hz and 4.6xx10^(15) Hz are inciden...
Text Solution
|
- In a historical experiment to dtermine Planck's constant, a metal surf...
Text Solution
|
- In a historical experiment to determine Planck's constant, a metal sur...
Text Solution
|
- प्लांक नियतांक ज्ञात करने के लिए एक ऐतिहासिक प्रयोग में एक धातु...
Text Solution
|
- In an experiment on photoelectric emission from a metallic surface ,wa...
Text Solution
|
- A stopping potential of 0.82 volt is required to stop the photoelectro...
Text Solution
|