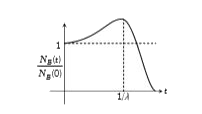
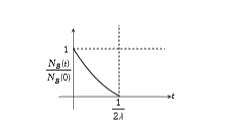
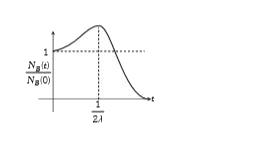
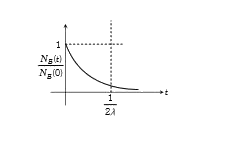
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- At time t = 0, a material is composed of two radioactive atoms A and B...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a radioactive disintegration according to the equation ArarrB...
Text Solution
|
- Nucleus A decays to B with decay constant lambda(1) and B decays to C ...
Text Solution
|
- Two radioactive materials A & B have decay constant 3lamda and 2lamda ...
Text Solution
|
- At time t = 0, a container has N(0) radioactive atoms with a decay con...
Text Solution
|
- एक रेडियोएक्टिव पदार्थ झिड़की अर्द्ध - आयु T है, में t = 0 पर परमाणुओं ...
Text Solution
|
- एक रेडियोएक्टिव पदार्थ झिड़की अर्द्ध - आयु T है, में t = 0 पर परमाणुओं ...
Text Solution
|
- Nucleus A decays into B with a decay constant lamda(1) and B further d...
Text Solution
|
- A radioactive sample has N(0) active atoms at t=0. If the rate of disi...
Text Solution
|