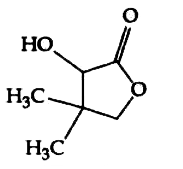
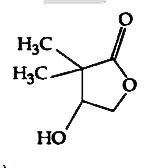
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Isobutyraldehyde on reaction with formaldehyde and K2CO3, gives compou...
Text Solution
|
- Propyl lithium reacts with ethene to give a compound (A), which on rea...
Text Solution
|
- A compound (A) of boron reacts with Nme(3) to give an adduct (B) which...
Text Solution
|
- Compound A on reduction gives B which on further reaction with CHCl(3)...
Text Solution
|
- A compound (A) of boron reacts with Nme(3) to give an adduct (B) which...
Text Solution
|
- Compound 'A' on chlorination gives compound 'B' , compound 'B' reacts ...
Text Solution
|
- A compound (A) of boron reacts with NMe(3) to give an adduct (B) which...
Text Solution
|
- A nitraite on acid hydrolysis gives compound A, which reacts with thio...
Text Solution
|
- Compound A (ester ) reacts with LiAlH4 gives B and C. Compound B on ox...
Text Solution
|