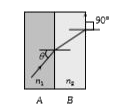
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A and B are two parallel sided transparent slabs of refractive indices...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical surface of radius 30 cm separates two transparent media A ...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical surface of radius 30cm separates two transparent media A ...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangular glass slab ABCD of refractive index n(1) is immersed in ...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure (a) the light is incident at an angle theta (slightly gr...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light incident on a slab of transparent material is partly re...
Text Solution
|
- n(1) तथा n(2) अपवर्तनांक के दो माध्यमों को अलग करने वाले उत्तल गोलीय...
Text Solution
|
- A,B, and C are the parallel sided transparent media of refractive indi...
Text Solution
|
- A light ray is incident at an angle 45∘ on parallel sided glass slab a...
Text Solution
|