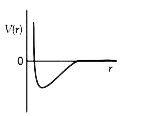
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- One mole of a monoatomic real gas satisfies the equation p(V-b)=RT wh...
Text Solution
|
- The equation of state for real gas is given by ((p + (a)/(V^(2))(V - b...
Text Solution
|
- The equation of a state of a real gas is given by (P + (a)/(V^(2))) (V...
Text Solution
|
- The van der waal's gas equation is (P+a/V^(2))(V-b)=RT, where P is pre...
Text Solution
|
- The equation of state of a real gas is given by (P+a/V^(2)) (V-b)=RT w...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of a monoatomic real gas satisfies the equation p(V-b)=RT whe...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of a monoatomic real gas satisfies the equation p(V -b) = RT ...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of a monoatomic gas satisfies the equation P(V-b)=RT Where b ...
Text Solution
|
- एक एक्परमाणुक वास्तविक गैस के एक मोल, समीकरण P(V-b)=RT संतुष्ट करती है...
Text Solution
|