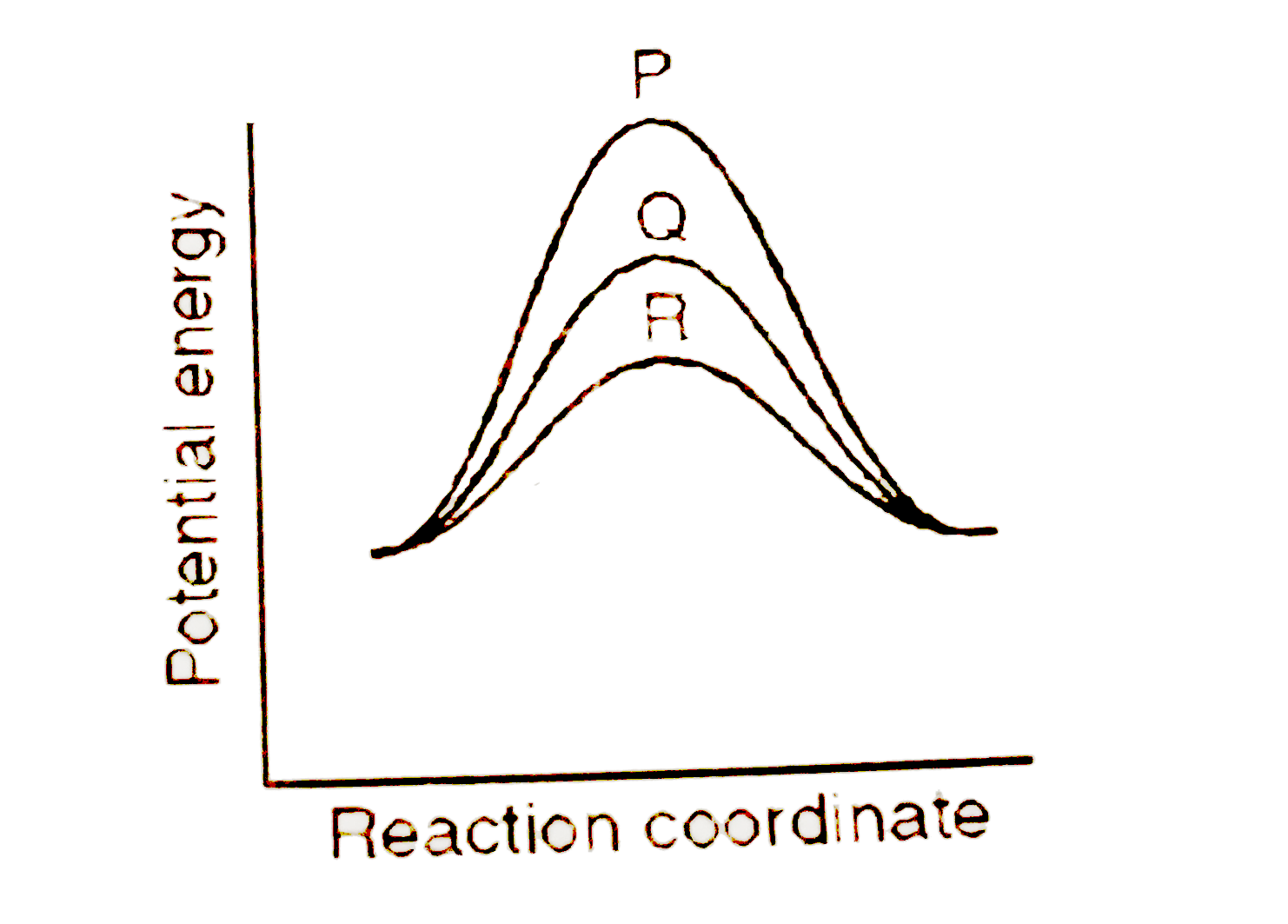
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- If a homogeneous catalytic reaction can take place through three alter...
Text Solution
|
- Substances which alter the velocity of a reaction by mere presence, wi...
Text Solution
|
- A homogenous catalytic reaction takes place through the three alternat...
Text Solution
|
- If a homogeneous catalytic reaction can take place through three alter...
Text Solution
|
- If a homogeneous catalytic reaction follows three alternative paths A,...
Text Solution
|
- In homogeneous catalytic reactions, the rate of reaction:
Text Solution
|
- A homogenous catalytic reaction takes place through the three alternat...
Text Solution
|
- If a homogeneous catalytic reaction can take place through three alter...
Text Solution
|
- यदि एक समांगी उत्प्रेरकीय अभिक्रिया नीचे दिए गए तीन अलग-अलग पथों से नि...
Text Solution
|