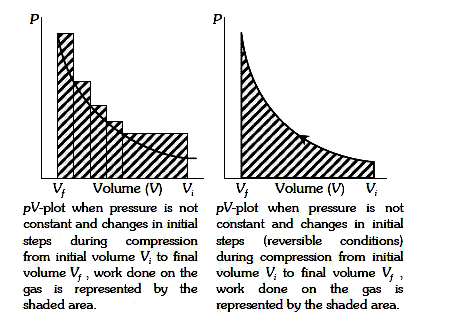A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The pressure volume work for an ideal gas can be calculated by using t...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas expands isothermally from volume V(1) to V(2) and is then...
Text Solution
|
- The pressure volume work for an ideal gas can be calculated by using t...
Text Solution
|
- The pressure-volume work for an ideal gas can be calculated by using t...
Text Solution
|
- The pressure -volume work for an ideal gas canbe calculated by using t...
Text Solution
|
- The pressure-volume work for an ideal gas can be calculated by using ...
Text Solution
|
- The pressure volume work for an ideal gas can be calculated by using t...
Text Solution
|
- What is the relation for work done (i) reversibly and (ii) irreversibl...
Text Solution
|
- The pressure-volume work for an ideal gas can be calculated by using t...
Text Solution
|