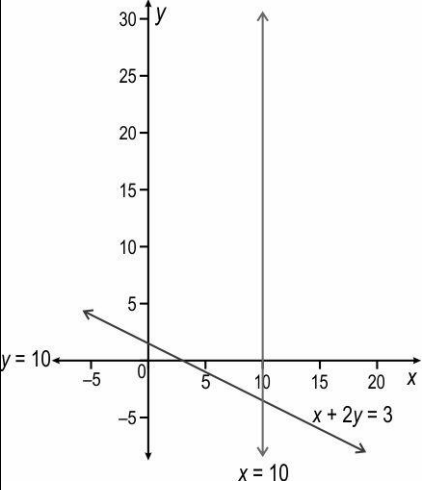
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CBSE MODEL PAPER-Additional Practice Questions-Question
- A linear programming problem (LPP) along with its constraints is given...
Text Solution
|
- M and N are two events such that P(M|N) = 0.3, P(M)= 0.2 and P(N) = 0....
Text Solution
|
- The constraints of a linear programming problem along with their graph...
Text Solution
|
- Shown is the graph of the function f:R - {0} rightarrow R defined b...
Text Solution
|
- Two statements are given below - one labelled Assertion (A) and the ot...
Text Solution
|
- cot^(-1)x = cos^(-1)(-1)- cosec^(-1) (frac{2}{sqrt 3}) Based on the ...
Text Solution
|
- (i) Find the domain of the function below. f(x) = frac{1}{2} sec^(-1...
Text Solution
|
- The matrix A = [[6, 8, 5],[4, 2, 3],[9, 7, 1]] is the sum of a symmetr...
Text Solution
|
- Find frac{dy}{dx} if y=(e^(sec x) + x)^4. Show your work.
Text Solution
|
- The position of vectors of the points P, Q and R are hat p, hat q and ...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure below, QRST and QRTP are parallelograms. Using the ...
Text Solution
|
- The vector equation of a line AB is given by vec r=x1(1 + lambda) hat ...
Text Solution
|
- Check whether the following statement is true or false. If u = e^(si...
Text Solution
|
- If frac{x^n}{y^n}=(xy)^(m-n), (y ne 0), find frac{dy}{dx}. Show your w...
Text Solution
|
- The anti-derivative of a function of the form (3x − 1)f(x), (x ne frac...
Text Solution
|
- Evaluate the following definite integral and show your work. intfrac...
Text Solution
|
- Find the particular solution when x = y = 0 for the following differen...
Text Solution
|
- Find the general solution of the following differential equation. (x...
Text Solution
|
- Frame the below optimisation problem as a linear programming problem a...
Text Solution
|
- Nikhil has a bag of marbles that contains exactly 8 green marbles and ...
Text Solution
|