Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
XII BOARDS PREVIOUS YEAR-QUESTION PAPER 2023-Question
- Assertion (A): When three electric bulbs of power 200 W, 100 W and 50 ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A): A current carrying square loop made of a wire of length...
Text Solution
|
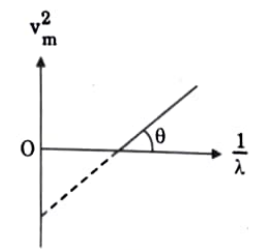
- The figure shows vm^2 versus 1/lambda raph for photoelectrons emitted ...
Text Solution
|
- Describe the process by which energy is released by the sun.
Text Solution
|
- Using Gauss’ law, derive an expression for the electric field at a poi...
Text Solution
|
- .A cell of emf E and internal resistance r is connected across a varia...
Text Solution
|
- Obtain an expression for electrostatic potential energy ofa system of ...
Text Solution
|
- Two small conducting balls A and B of radius r1 and r2 have charges q1...
Text Solution
|
- What is a displacement current ? How is it different from a conduction...
Text Solution
|
- Write any two characteristics of an electromagnetic wave. Why are micr...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Draw a plot showing the variation of potential energy of a pair of...
Text Solution
|
- A current carrying circular loop and a straigbt wire bent partly in th...
Text Solution
|
- (i) In diffraction due to a single slit, the phase difference between ...
Text Solution
|
- (i)In a Young's double-slit experiment SS2-SS1=lambda/4,where S1 and S...
Text Solution
|
- A resistor of 30 ohm and a capacitor of 250/pi muF are connected in se...
Text Solution
|
- A Series LCR circuit with R = 20 ohm,L=2H and C=50muF is connected to ...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangular conductor MNPQ with a movable arm MN (resistance r) is k...
Text Solution
|
- (i) Define mobility of electrons. Give its SI units. (ii) A steady cur...
Text Solution
|
- (i) Define electrical conductivity of a wire. Give its SI unit. (ii) H...
Text Solution
|
- (i) Explain the working principle of an optical fibre with the help of...
Text Solution
|