Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
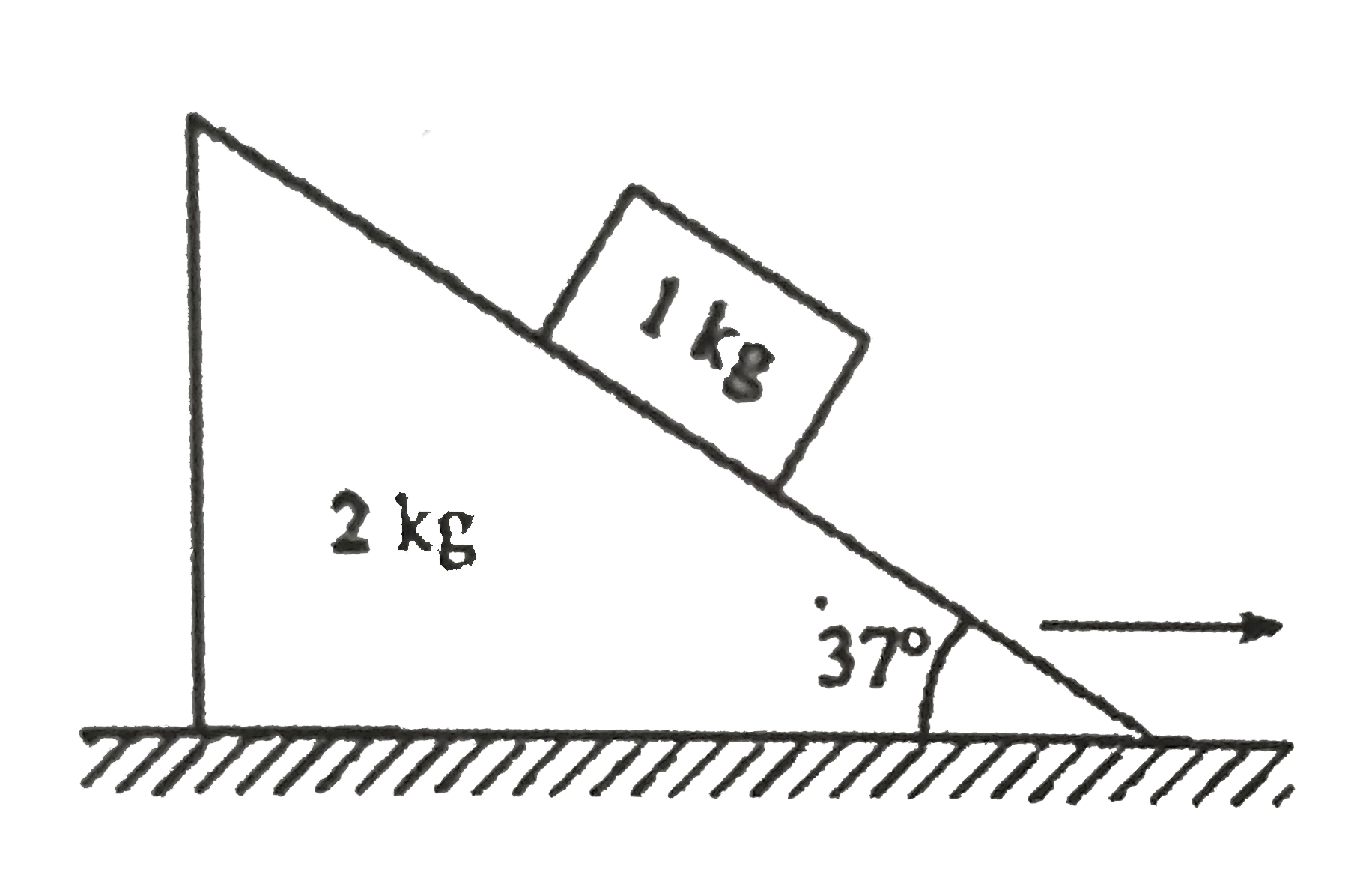
- Figure-2.162 shows a wedge of mass 2kg resting on a fritionless floor....
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 1 kg is at rest relative to a smooth wedge moving left...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 2kg slides down the face of a smooth 45^@ wedge of mas...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is placed on a smooth inclined wedge ABC of inclinat...
Text Solution
|
- Two small blcok m=2kg each kept on wedge of mass 12 kg . There is no f...
Text Solution
|
- Figure-2.162 shows a wedge of mass 2kg resting on a fritionless floor....
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 2 kg is kept on a smooth wedge of mass 3 kg and wedge ...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement shown in the fig. the block of mass m lies on the w...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement shown in the fig. the block of mass m lies on the w...
Text Solution
|