Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
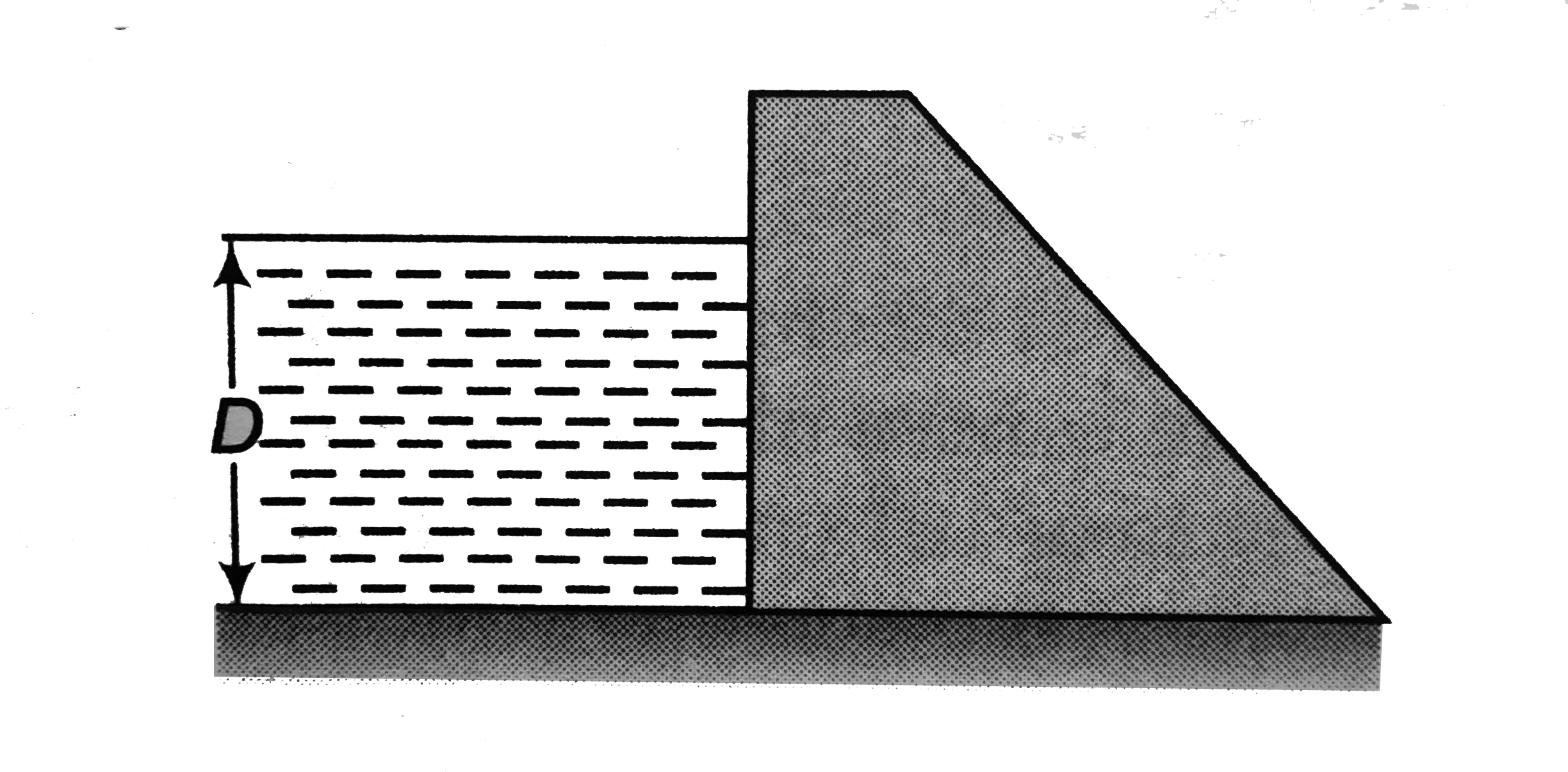
- Water stands at a depth D behind the vertical upstream face of a dam a...
Text Solution
|
- Water stands at a depth D behind the vertical upstream face of a dam a...
Text Solution
|
- Water stands at a depth h behind the vertical face of a dam. It exerts...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a cross sectional view of a masonry dam whose length per...
Text Solution
|
- Water stands at a depth of 15 m behind a reservoir dam. A horizontal p...
Text Solution
|
- Water stands upto a height h behind the vertical wall of a dam what is...
Text Solution
|
- In a dam , the surface water is at higher temperature than the water d...
Text Solution
|
- Water stands upto height h behind the dam as shown in the figure. The ...
Text Solution
|
- In Fig ., the fresh water stands at depth D = 30.0 m behind the vertic...
Text Solution
|