Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
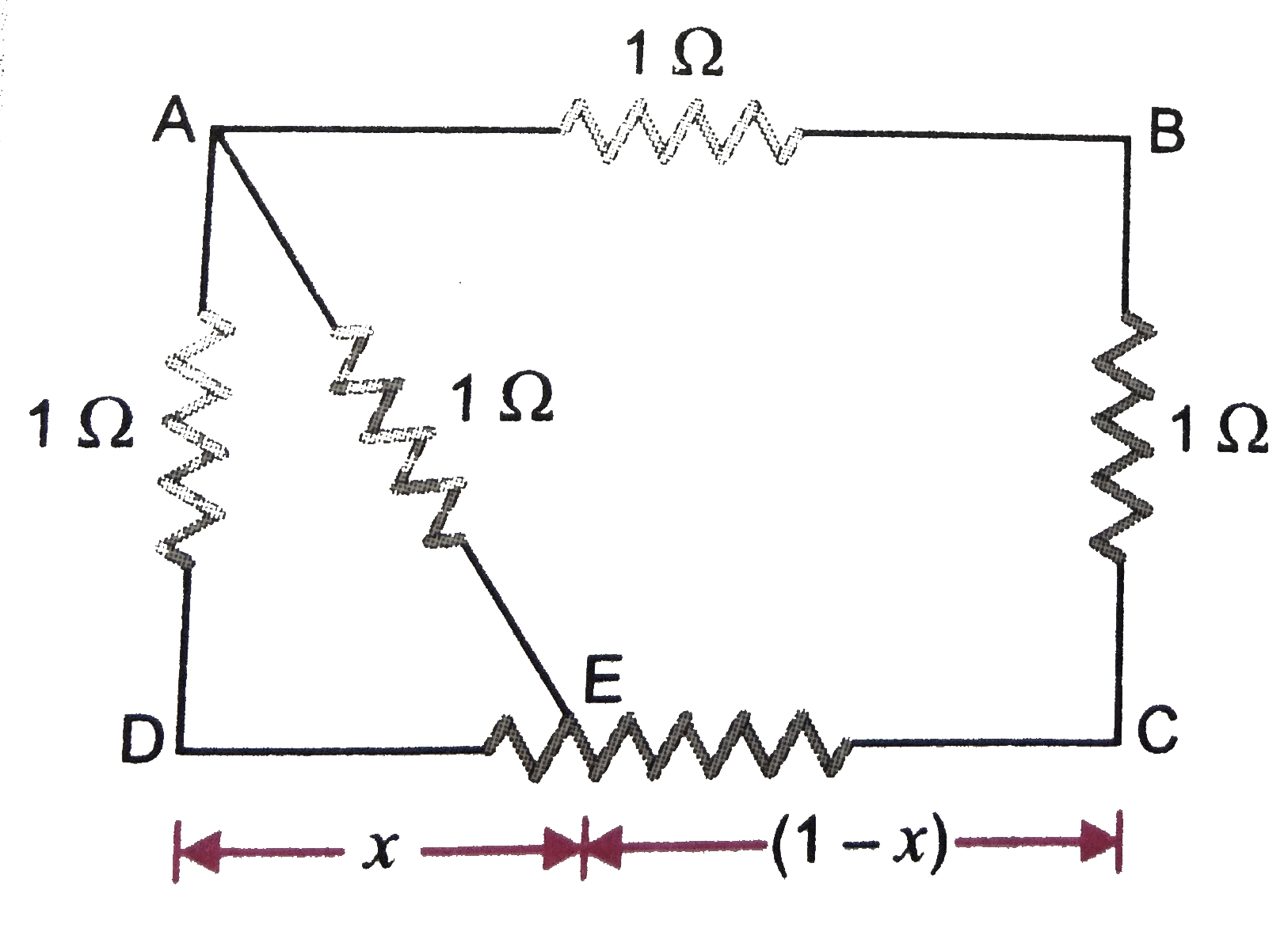
- ABCD is a square where each side is a uniform wire of resistance 1 Ome...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform wire of resistance 18 Omega is bent in the form of a circle....
Text Solution
|
- ABCD is a square where each side is a uniform wire of resistance 1Omeg...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform wire of resistance 9 Omega is cut into 3 equal parts. They a...
Text Solution
|
- ABCD is a square where each side is a uniform wire of resistance 1 Ome...
Text Solution
|
- In figure. ABCD is a square where side is a uniform wire of resistance...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform wire of resistance 36 Omega is bent in the form of a circle....
Text Solution
|
- A potential difference of 100 V is applied across a wire of resistance...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform wire os resistance 12 Omega is bent to form a circle. Effect...
Text Solution
|