Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
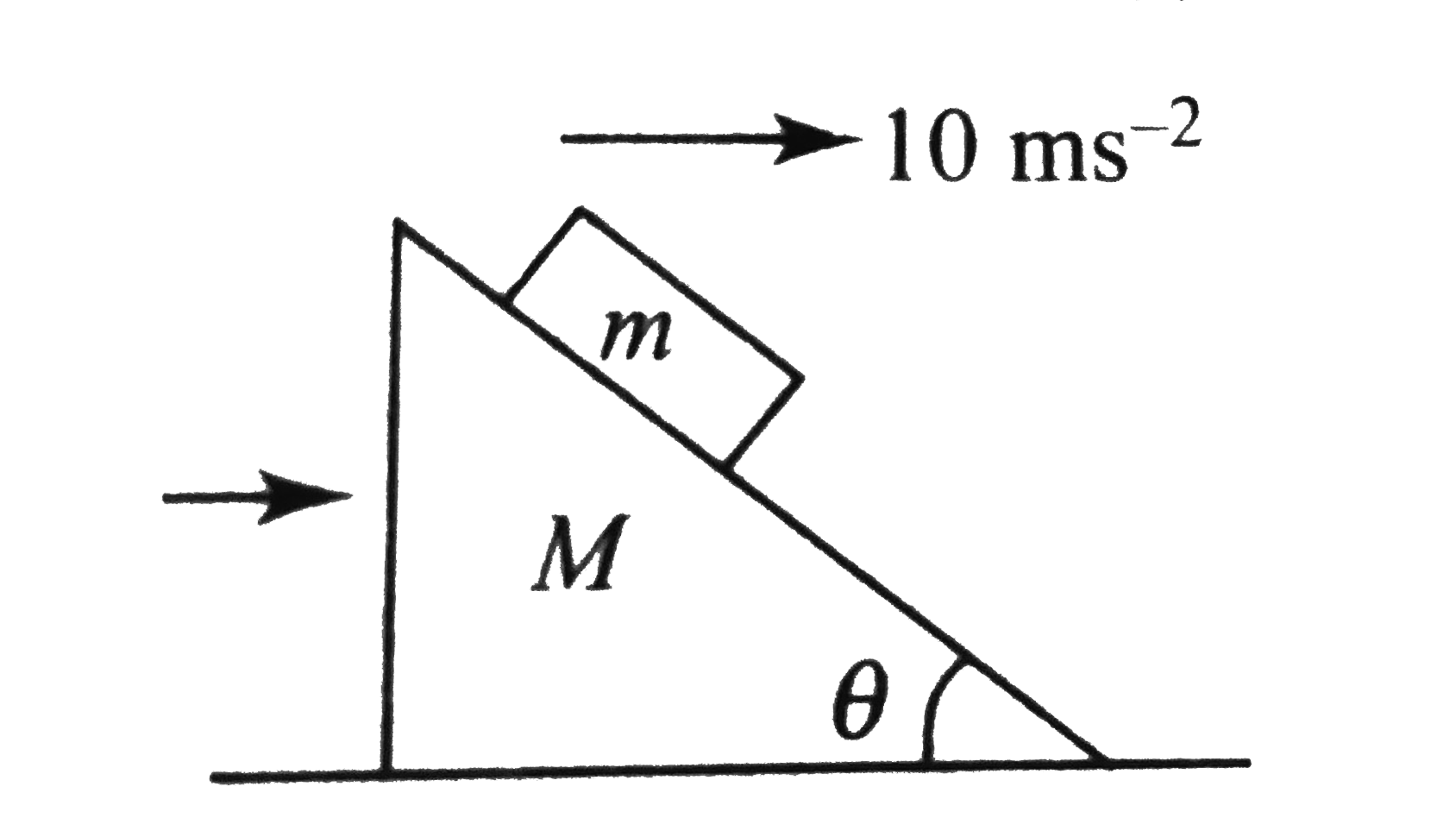
- In figuer, shown all the surfaces are frictionless, and mass of the bl...
Text Solution
|
- In figuer, shown all the surfaces are frictionless, and mass of the bl...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is placed on a smooth wedge of inclination. The whol...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown all the surfaces are frictionless and mass of bloc...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is placed on a smooth wedge of inclination theta . T...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is placed on a smooth wedge of inclination theta. T...
Text Solution
|
- A wedge of mass M makes an angle theta with the horizontal. The wedge ...
Text Solution
|
- As shown in the figure a block of mass 'm' is placed on a smooth wedge...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is placed on a smooth wedge of wedge angle theta The...
Text Solution
|