Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
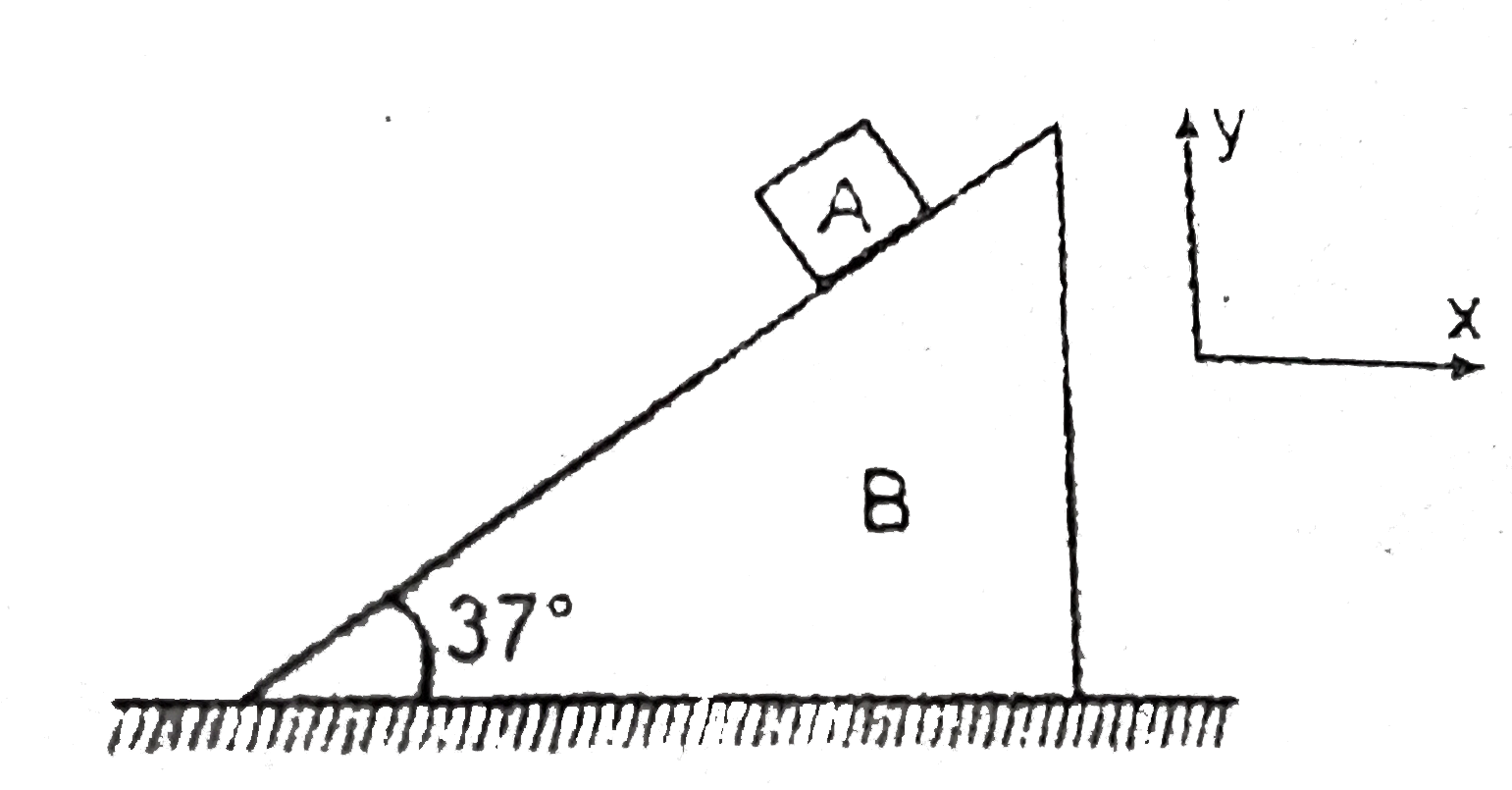
- In the figure shown the acceleration of A is, vec(a)(A) = 15 hat (i) +...
Text Solution
|
- If vec a= hat i- hat j\ a n d\ vec b=- hat j+ hat k find the project...
Text Solution
|
- vec a = (hat i + hat j + hat k), vec a * vec b = 1 and vec a xxvec b =...
Text Solution
|
- A charged particle has acceleration vec a = 2 hat i + x hat j in a meg...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown the acceleration of A is, vec(a)(A) = 15 hat (i) +...
Text Solution
|
- यदि vec(a)=hat(i)+hat(j)+hat(k),vec(b)=2hat(i)-hat(j)+3hat(k)" और "vec...
Text Solution
|
- If vec(a)=hat(i)-hat(j),vec(b)=hat(j)-hat(k),vec(c)=hat(k)-hat(i)" the...
Text Solution
|
- If vec(A) = hat(i) + hat(j) + hat(k) and B = -hat(i) - hat(j) - hat(k)...
Text Solution
|
- Let vec a= hat i+ hat j ; vec b=2 hat i- hat kdot Then vector vec r ...
Text Solution
|