Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
THERMODYNAMICS
PRADEEP|Exercise Sample Problem 3|1 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS
PRADEEP|Exercise Sample Problem 4|1 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS
PRADEEP|Exercise Sample Problem 1|6 VideosSTRUCTURE OF ATOM
PRADEEP|Exercise Competition Focus (JEE (Main and Advanced)/Medical Entrance (IX. Assertion And Reason Type Questions (Type II))|12 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-THERMODYNAMICS-Sample Problem 2
- 5.6dm^(3) of an unknown gas at S.T.P requires 52.25J of heat to raise ...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the amount of heat evolved when (i) 500 cm^(3) of 0.1 M h...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the enthalpy of formation of carbon monoxide (CO) from the f...
Text Solution
|
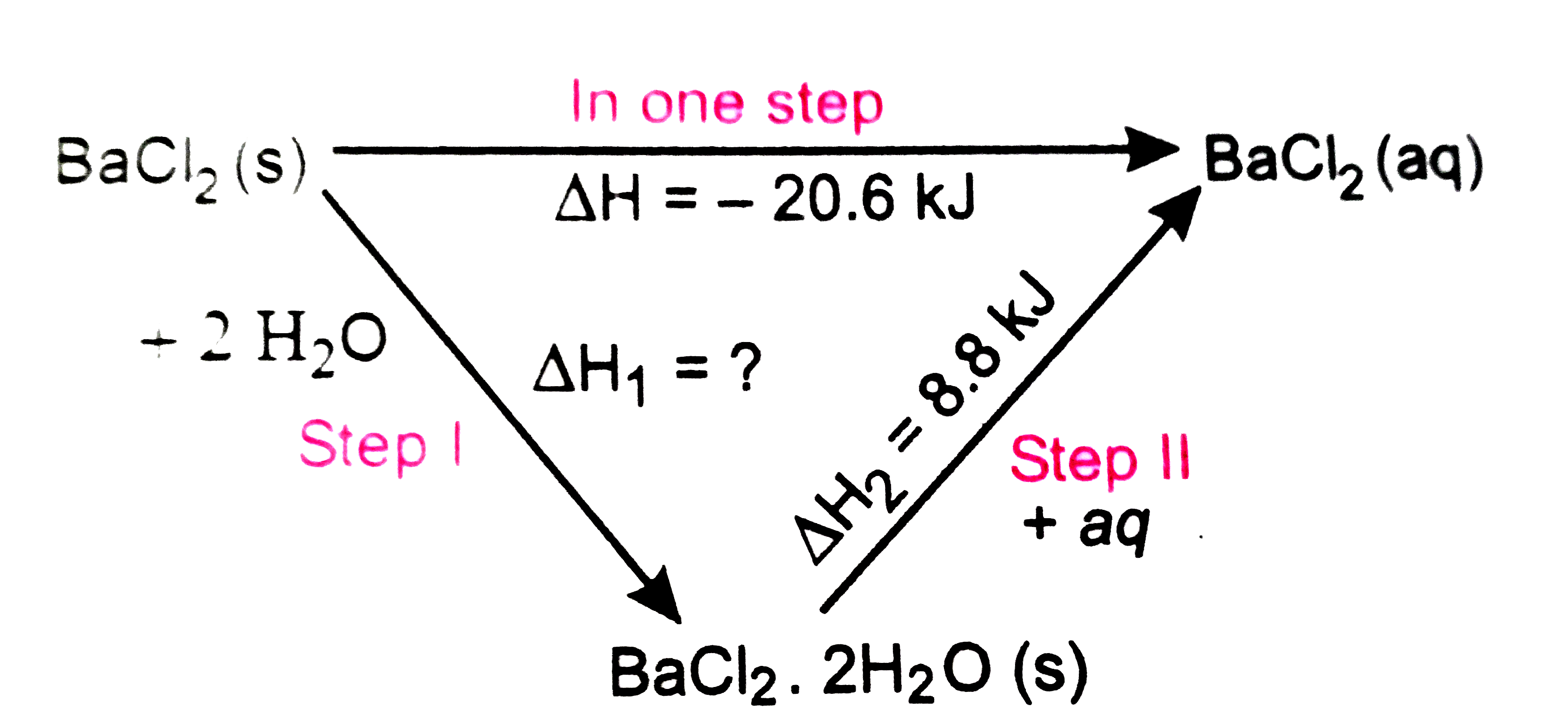
- Enthalpies of solution of BaCI(2). 2H(2)O and BaCI(2) are 8.8 and -20....
Text Solution
|
- Predict the sign of entropy change in each of the following : (i) H(...
Text Solution
|