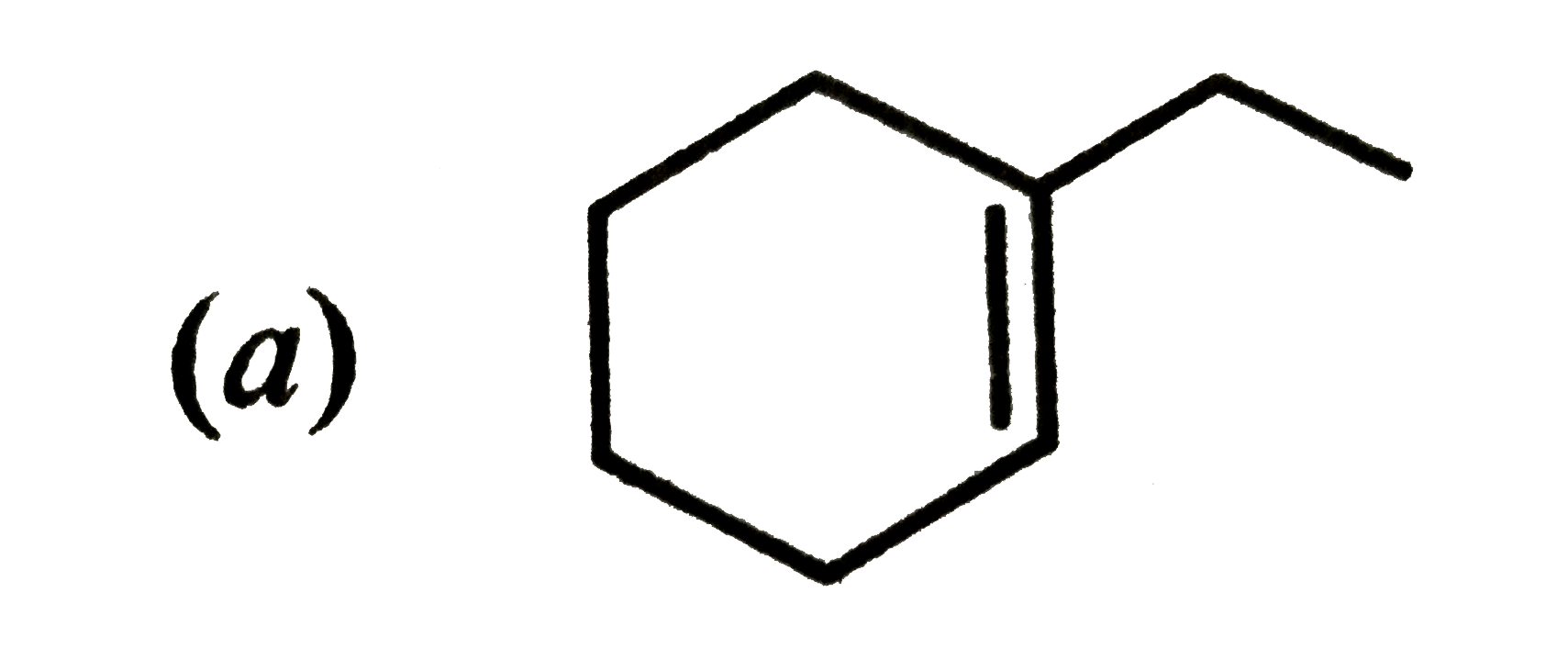
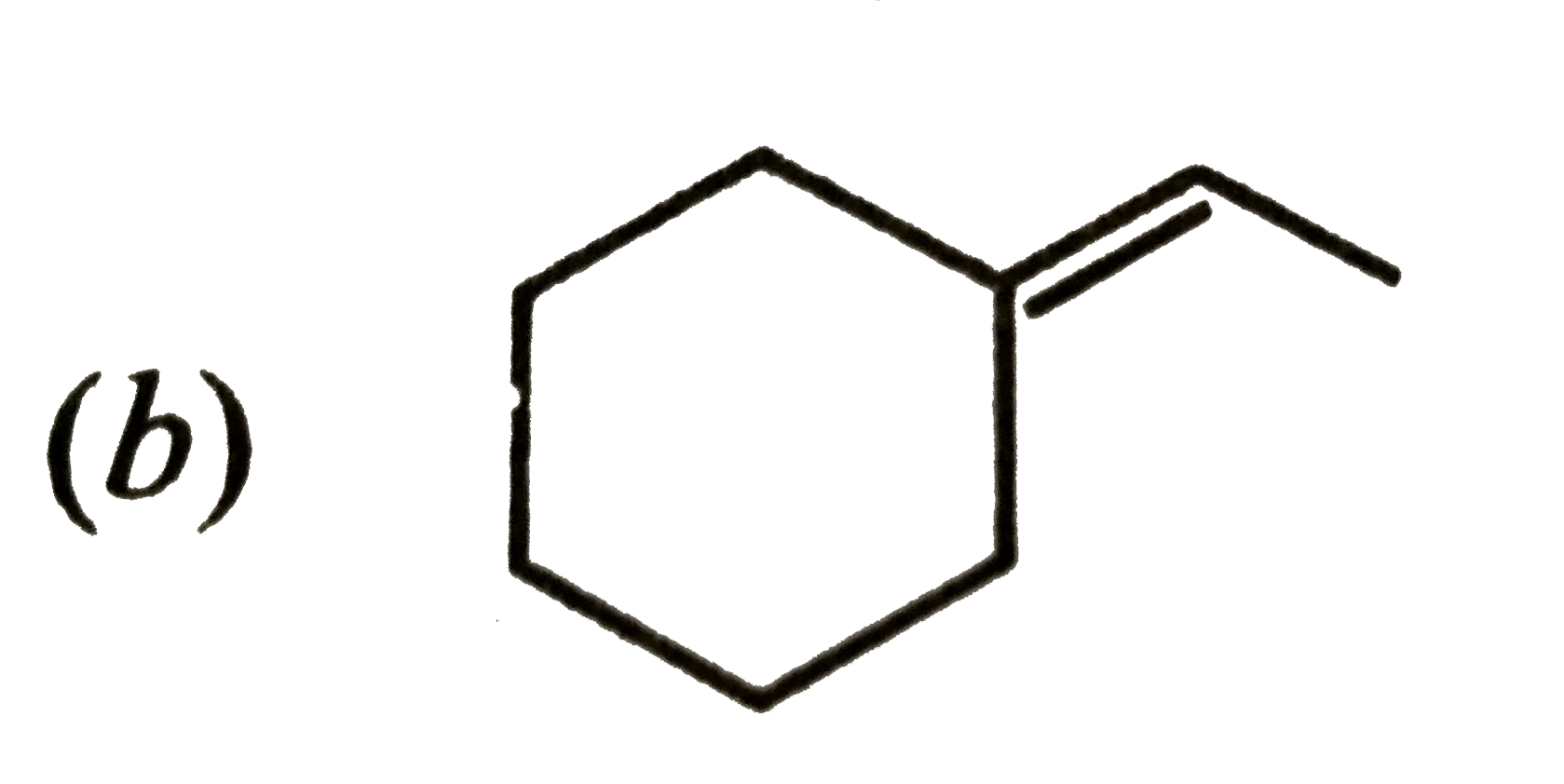
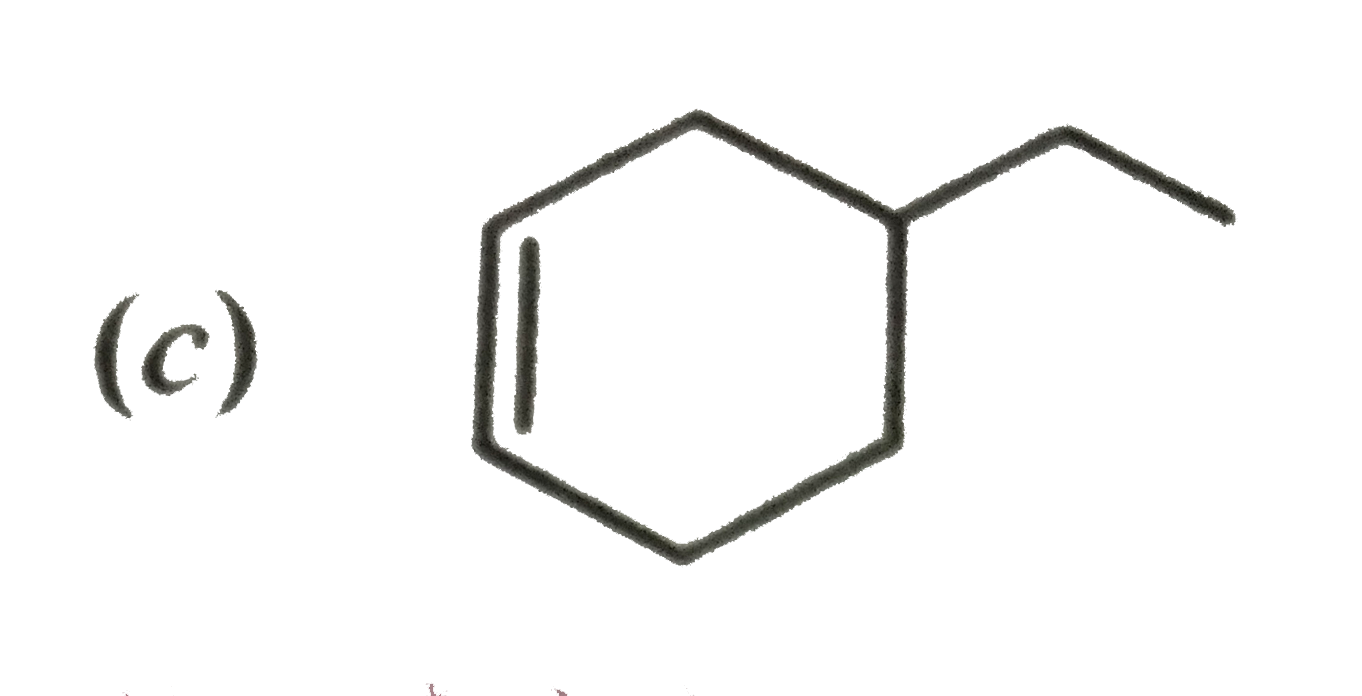
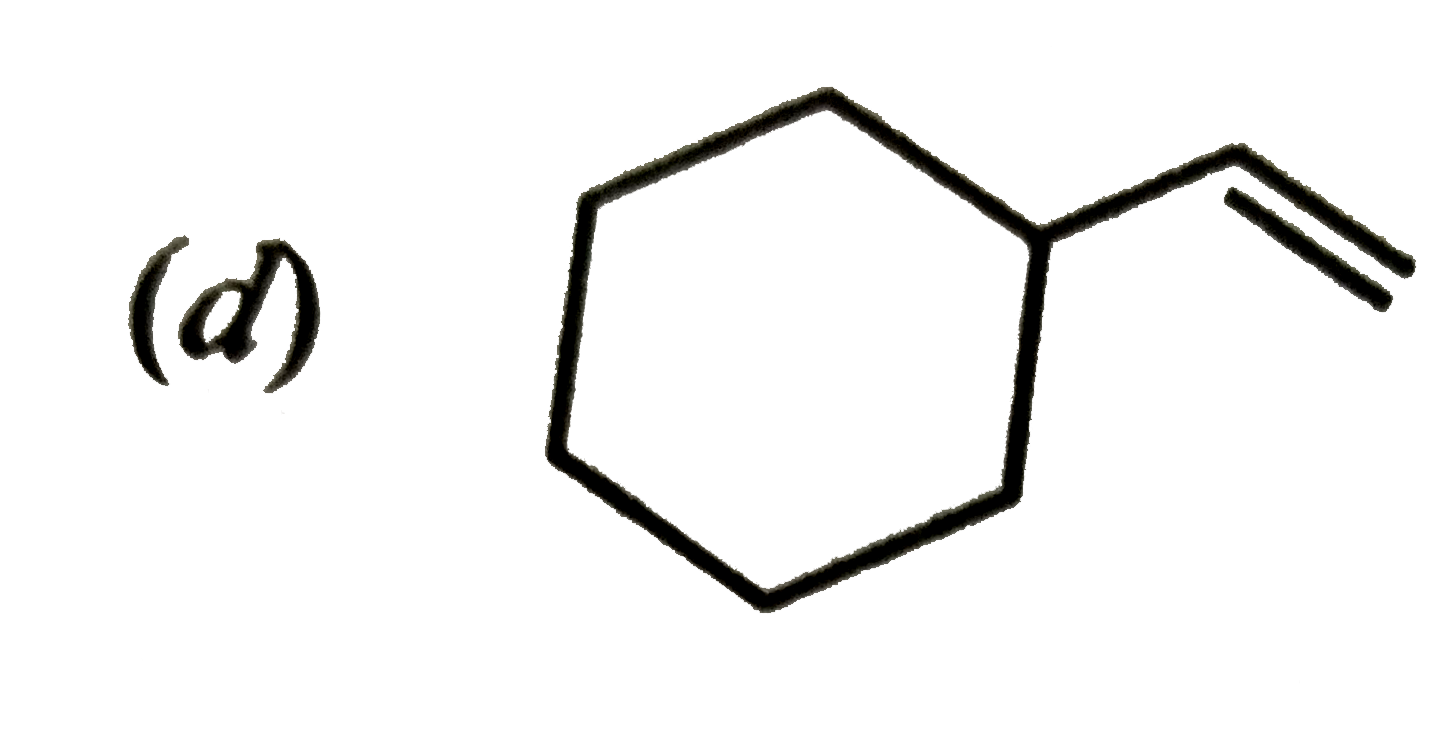
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
HYDROCARBONS
PRADEEP|Exercise Competition Focus (JEE(main and advanced)/Medical Entrance) IV. MATCHING TYPE QUESTIONS|3 VideosHYDROCARBONS
PRADEEP|Exercise Competition Focus (JEE(main and advanced)/Medical Entrance) V. MATRIX-MATCH TYPE QUESTIONS|1 VideosHYDROCARBONS
PRADEEP|Exercise Competition Focus (JEE(main and advanced)/Medical Entrance) II. MULTIPLE CHOICE|14 VideosEQUILIBRIUM IN PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROCESSES
PRADEEP|Exercise Competition Focus (Jee(Main and advanced)/Medical Entrance) VIII. ASSERTION - REASON TYPE QUESTIONS (TYPE - II)|10 VideosHYDROGEN
PRADEEP|Exercise COMPETITION FOCUS (Assertion-Reason Type Questions) Type 2|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-HYDROCARBONS-Competition Focus (JEE(main and advanced)/Medical Entrance) III. MULTIPLE CHOICE
- Catalytic hydrogenation involves addition of hydrogen to a gt C = Clt ...
Text Solution
|
- Catalytic hydrogenation involves addition of hydrogen to a C = C or -...
Text Solution
|
- Catalytic hydrogenation involves addition of hydrogen to a C = C or -C...
Text Solution
|
- Catalytic hydrogenation involves addition of hydrogen to a gt C = Clt ...
Text Solution
|
- Aromatic hydrocarbons are highly unsaturated molecules but behave lik...
Text Solution
|
- Aromatic hydrocarbons are highly unsaturated molecules but behave lik...
Text Solution
|
- Aromatic hydrocarbons are highly unsaturated molecules but behave lik...
Text Solution
|
- Aromatic hydrocarbons are highly unsaturated molecules but behave lik...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is not aromatic ?
Text Solution
|
- Which one of these is not compatible with arenes
Text Solution
|
- Identify the correct order of reactivity in electrophilic substitution...
Text Solution
|
- Ethylbenzene with bromine in the presence of FeBr(3) predominantly giv...
Text Solution
|
- Match the following columns
Text Solution
|
- The correct order towards electrophilic substitution is
Text Solution
|