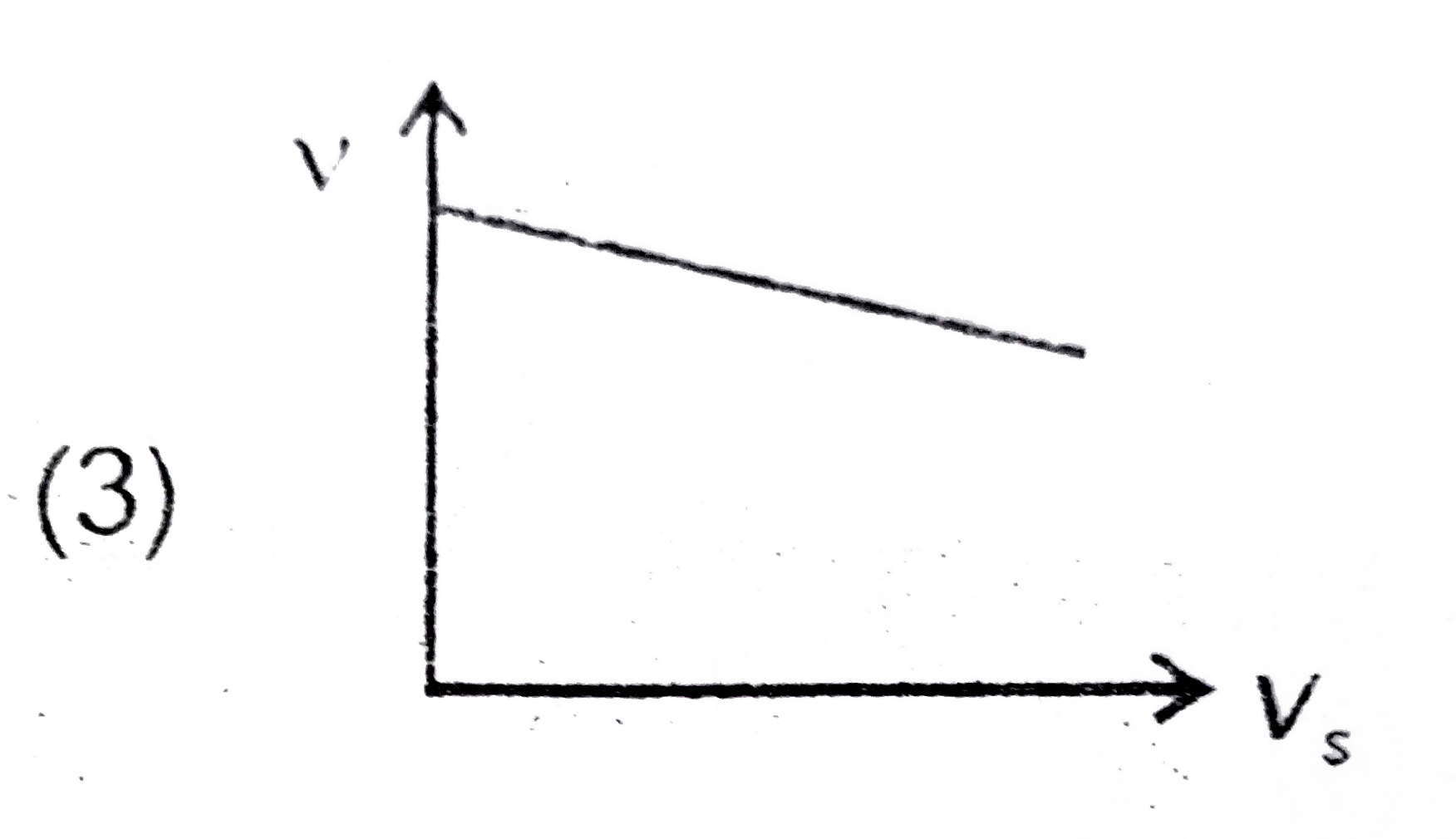
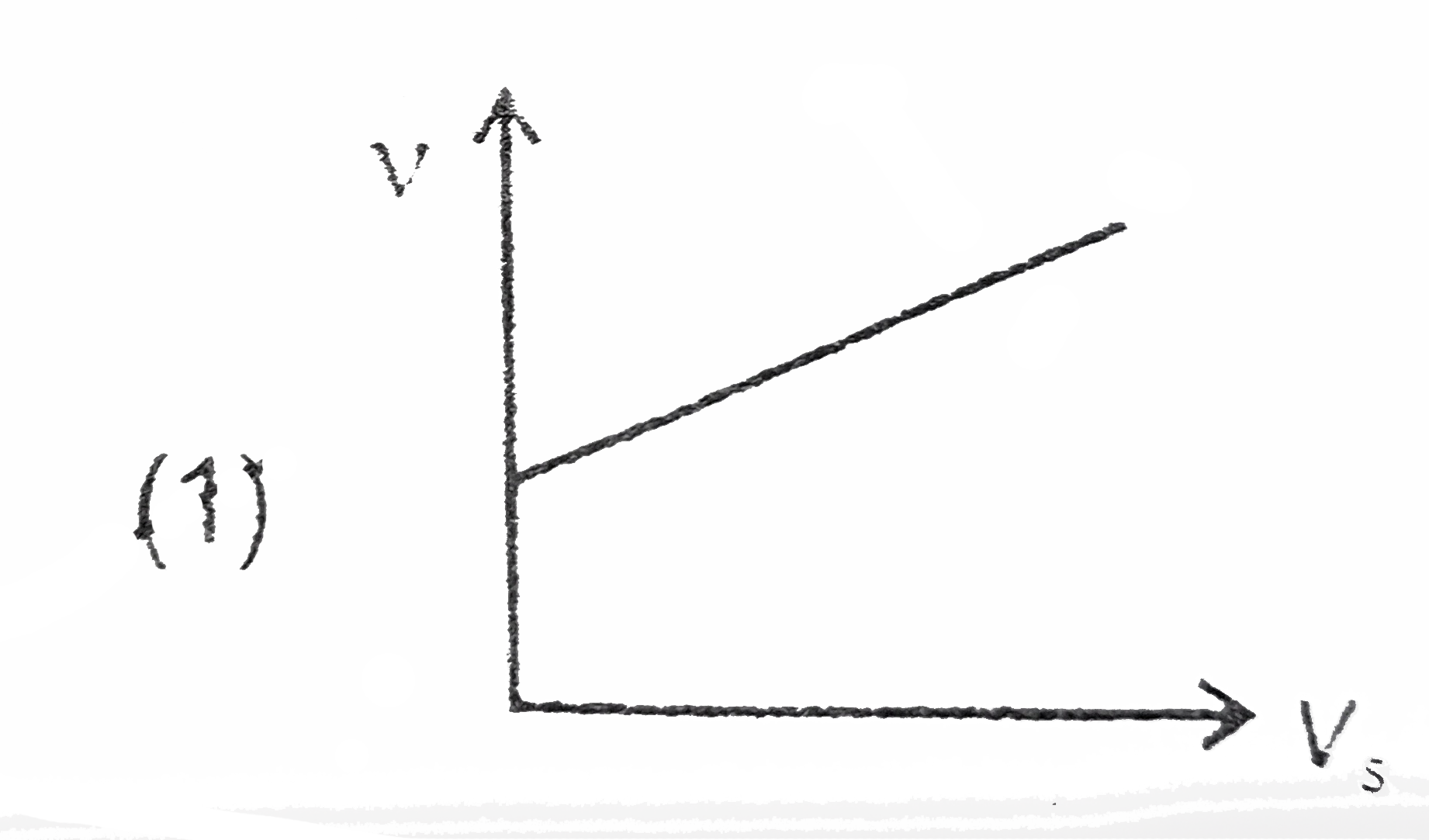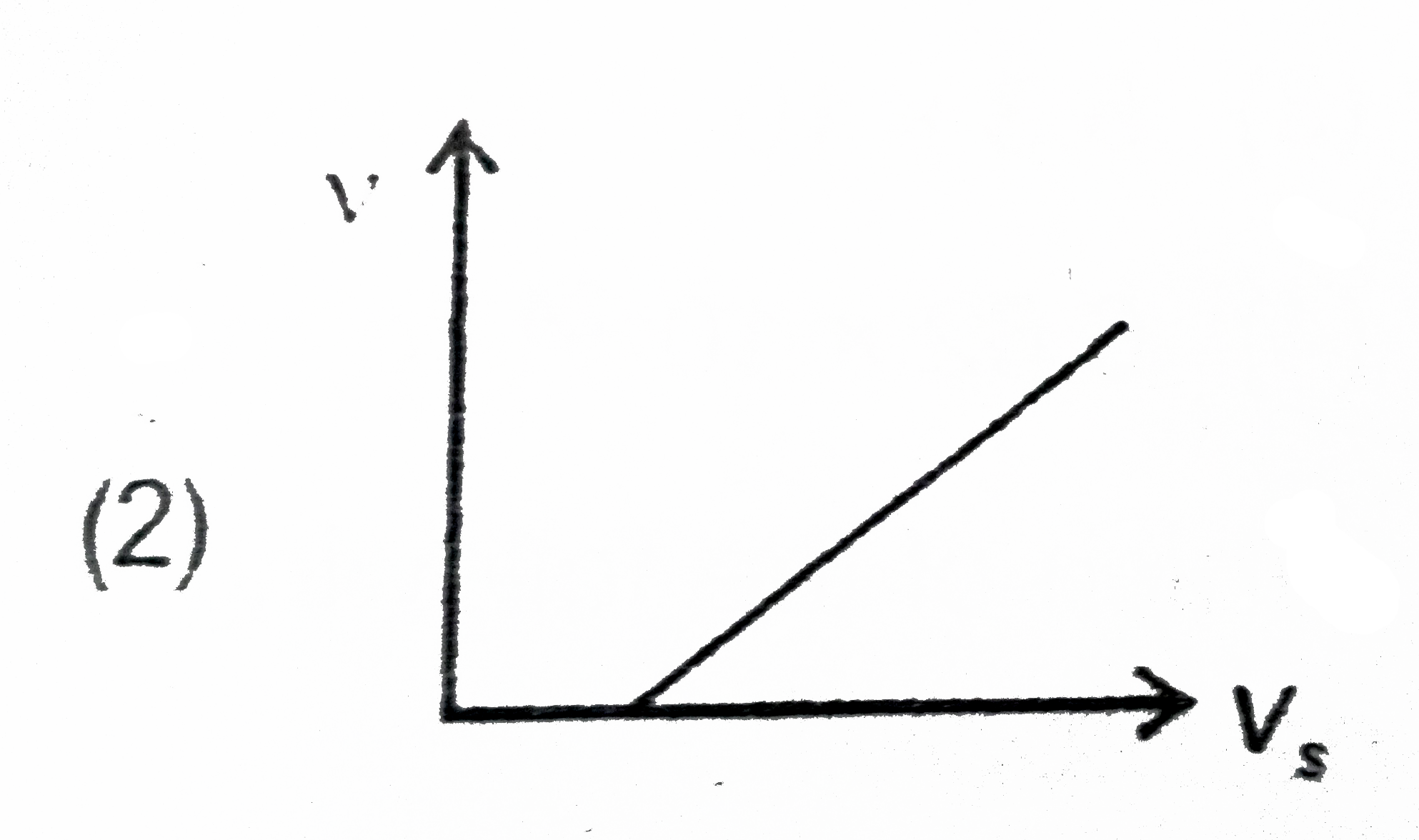A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
STRUCTURE OF ATOM
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise ASSIGNMENT ( SECTION -C) Objective Type Questions (More than one options are correct)|15 VideosSTRUCTURE OF ATOM
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise ASSIGNMENT ( SECTION -D) Linked Comprehension Type Questions)|9 VideosSTRUCTURE OF ATOM
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise ASSIGNMENT ( SECTION -A) Objective Type Questions (One option is correct)|47 VideosSTRUCTURE OF ATOM
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise ASSIGNMENT (SECTION -D) Assertion-Reason Type Questions|15 VideosSURFACE CHEMISTRY
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise Assignment Section - C (Assertion - Reason type questions)|10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH INSTITUTE-STRUCTURE OF ATOM -ASSIGNMENT ( SECTION -B) Objective Type Questions (One option is correct)
- With increasing principal quantum number , the energy difference betwe...
Text Solution
|
- H(α) line of Balmer series is 6500 Å . The wave length of H(gamma) is
Text Solution
|
- Graph of incident freuency with stopping potential in photoelectric ef...
Text Solution
|
- The orbital diagram in which Hund's rule and Aufbau principle is viola...
Text Solution
|
- The total spin resulting from d^(9) configuration is
Text Solution
|
- How many nodal planes are present in 4d(z^(2)) ?
Text Solution
|
- An electron is moving in 3^(rd) orbit of Li^(+2) and its separation e...
Text Solution
|
- If radius of 2^(nd) orbit is x then di-Broglie wavelength in4^(th)orbi...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the wavelength of light required to break the bond between t...
Text Solution
|
- An electron is moving in 3rd orbit of Hydrogen atom . The frequency of...
Text Solution
|
- The wavelength of a spectral life for an electronic transition inverse...
Text Solution
|
- In the Rutherford scattering experiment the number of alphaparticles s...
Text Solution
|
- The number of quanta of radiation of frequncy 4.98 xx 10^(14) s^(-1) r...
Text Solution
|
- Photoelectric emmision is observed from a surface when lights of freq...
Text Solution
|
- The velocity of electron moving in 3rd orbit of He^(+) is v. The veloc...
Text Solution
|
- Which electronic configuration is not allowed for a neutral atom or an...
Text Solution
|
- If E(1) , E(2) "and" E(3) represent respectively the kinetic energies ...
Text Solution
|
- Choose the correct statement
Text Solution
|
- Consider psi (wave function) of 2s atomic orbital of H-atom is- psi...
Text Solution
|
- In which of the following, maximum wavelength is emitted ?
Text Solution
|