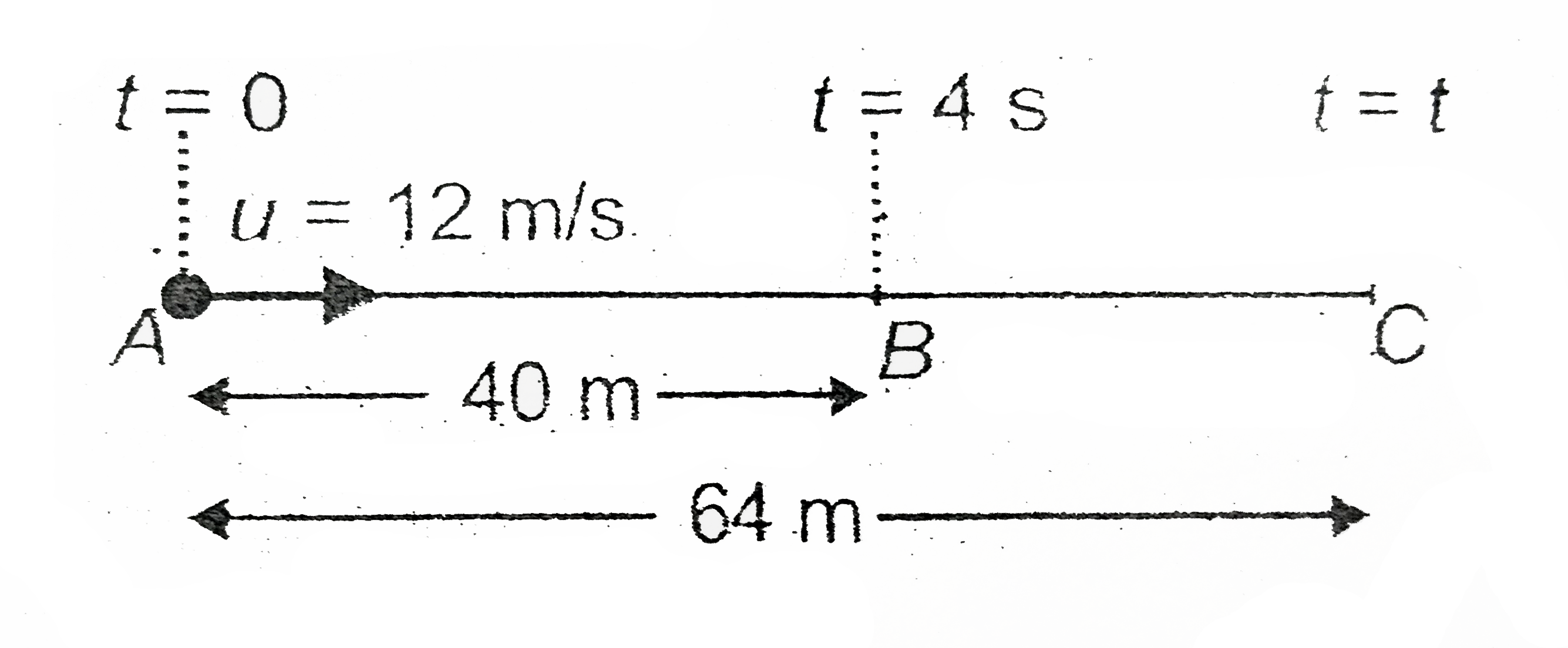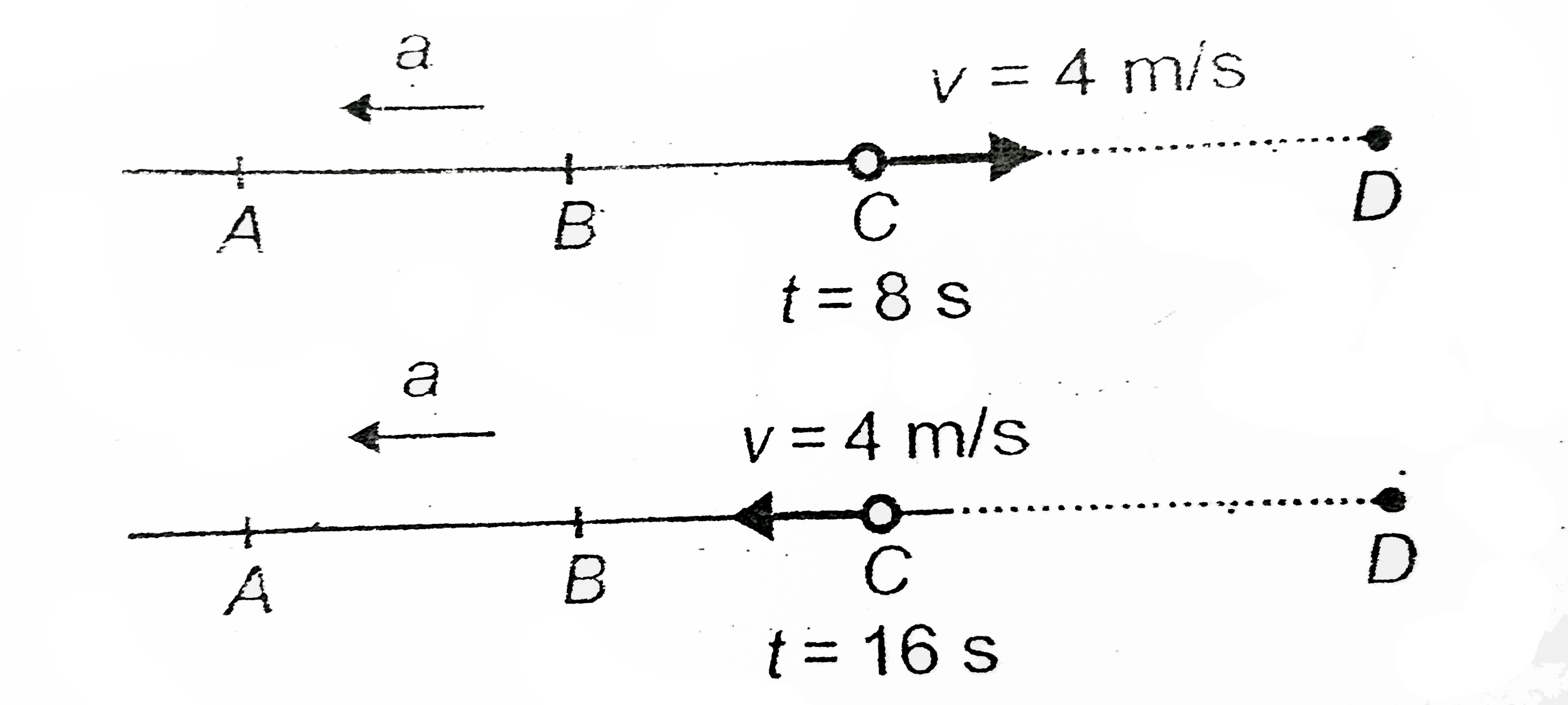(a) Let the acceleration of particle be a.
For motion between A and B
`u=12m//s, s=40 m, t=4s`
Using `s=ut+(1)/(2)at^(2)`, we get
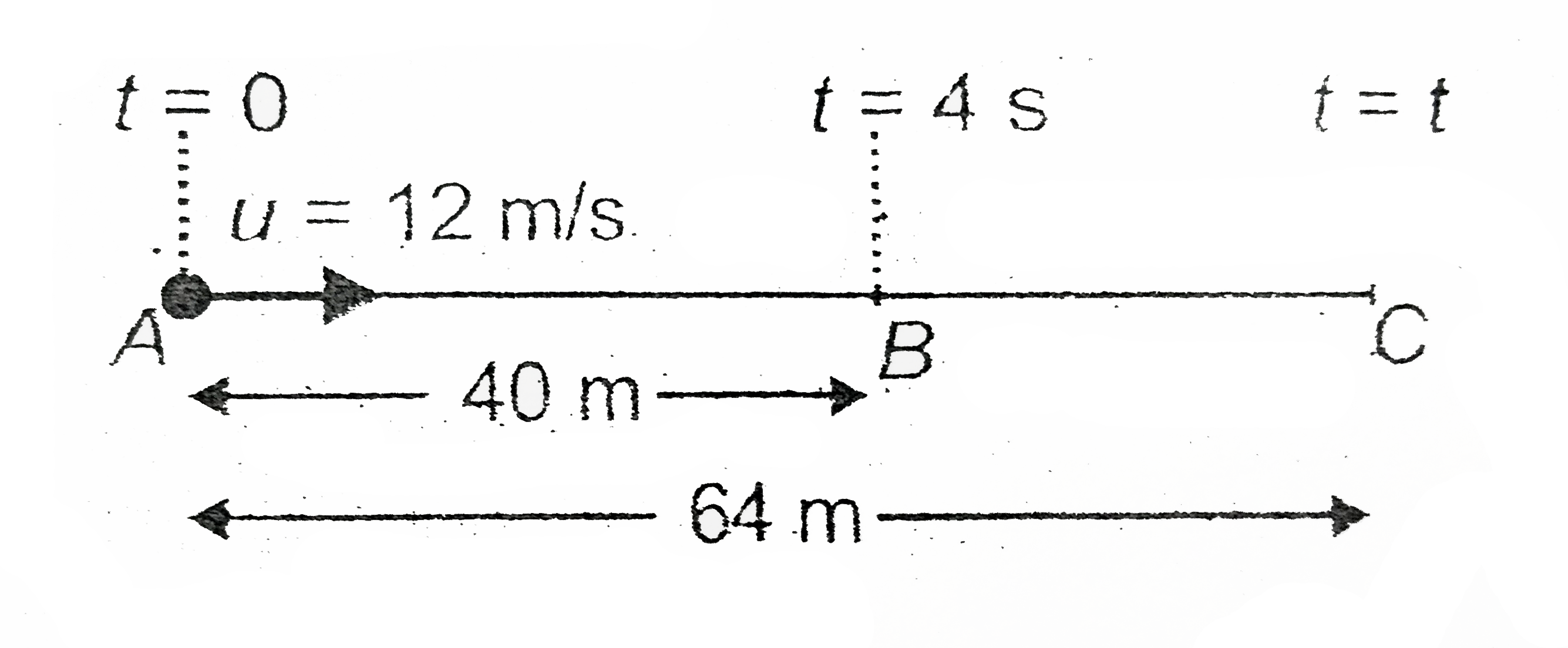
`40=12(4)+(1)/(2)a(4)^(2)`
`rArr a=-1m//s^(2)`
For motion between A and C
Let particle reaches C at time t.
`u=12m//s, s=64 m`
`rArr 64=12t+(1)/(2)(-1)t^(2)`
`rArr t^(2)-24t+128=0`
`rArr (t-8)(t-16)=0`
`rArr t=8s and t=16s` (why double answer?)
`rArr` The particle will be at C twice, at t = 8 s and t = 16 s.
(b) Velocityk of particle at C :
At t = 8 s, velocity at C is given by `v=12+(-1)xx8=4m//s`
and at t = 16 s velocity of particle is given by `v=12+(-1)xx16-4m//s`
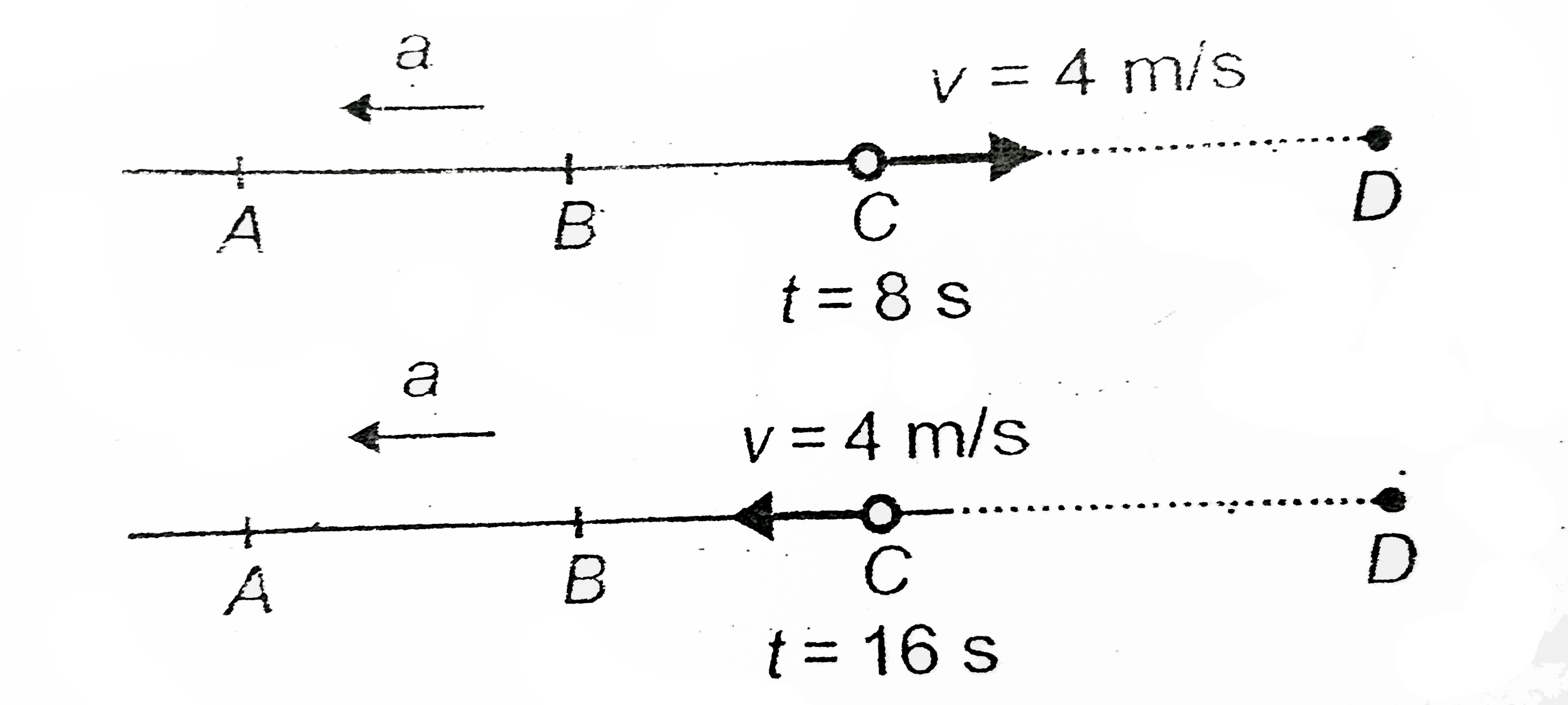
As the acceleration of particle is opposite to velocity, its speed decreases as it moves along ABC. At a point beyond C (say at D), the particle will come to rest momentarily, and then it will move backward with increasing speed and crosses point C again. This explains the double answer for time in part (a).