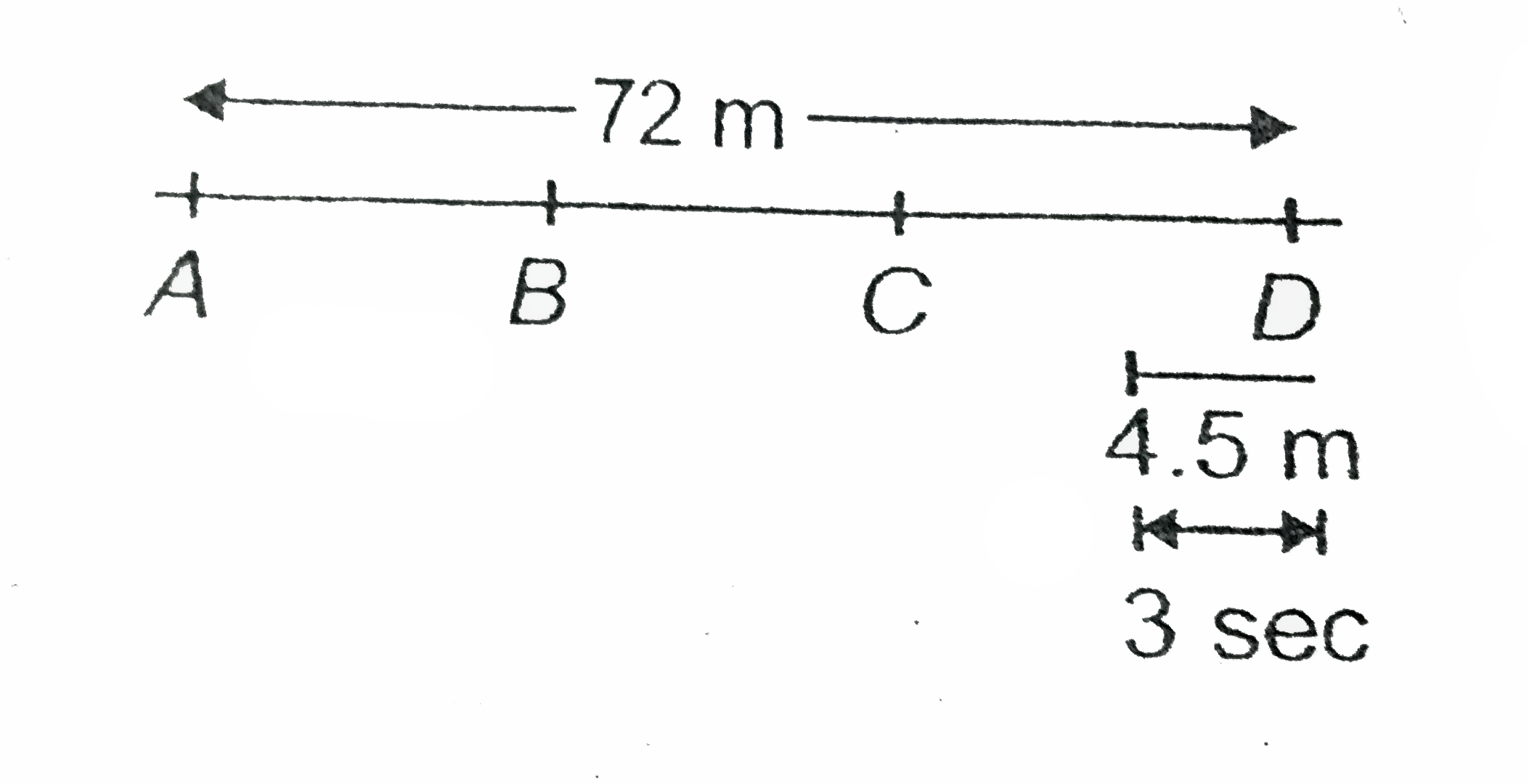(a) When the particle reaches the point A again, say at time t, its displacement is zero.
`rArr 0=ut+(1)/(2)at^(2)`
`rArr 0=12t+(1)/(2)(-1)t^(2)`
`rArr t=0 and =24s`
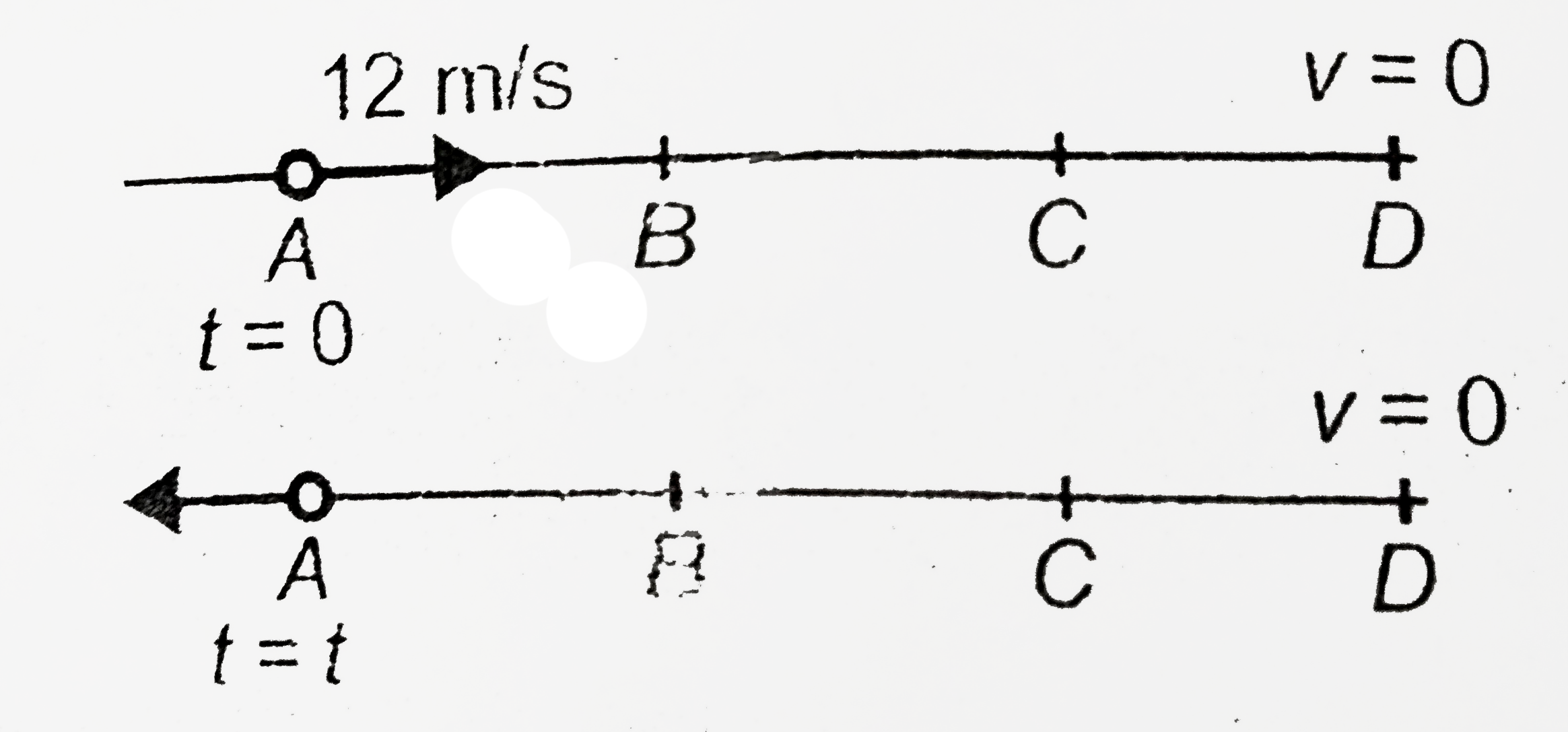
As t = 0 is the initial moment, t = 24 s is the moment when the particle reaches. A again
(b) Let the particle reverse its direction of motion at D, then the speed of particle at D will be zero. For the interval A to D
`u=12m//s, a=-1m//s^(2), AD=s, v=0`
`rArr 0^(2)=(12)^(2)+2(-1)(s)" "["from "v^(2)=u^(2)+2as]`
Ypu can also calculate the time taken by the particle to reach D from `v=u+at,0=12+(-1)t_(D)` and then from `s=12dt_(D)+(1)/(2)(-1)t_(D)^(2)`, you can find s. But then again you must be interested in optimizing the steps of calulation and must not proceed in the above manner.
(c) Can you use the equation `s=ut+(1)/(2)at^(2)` to find the distance travelled in the interval?
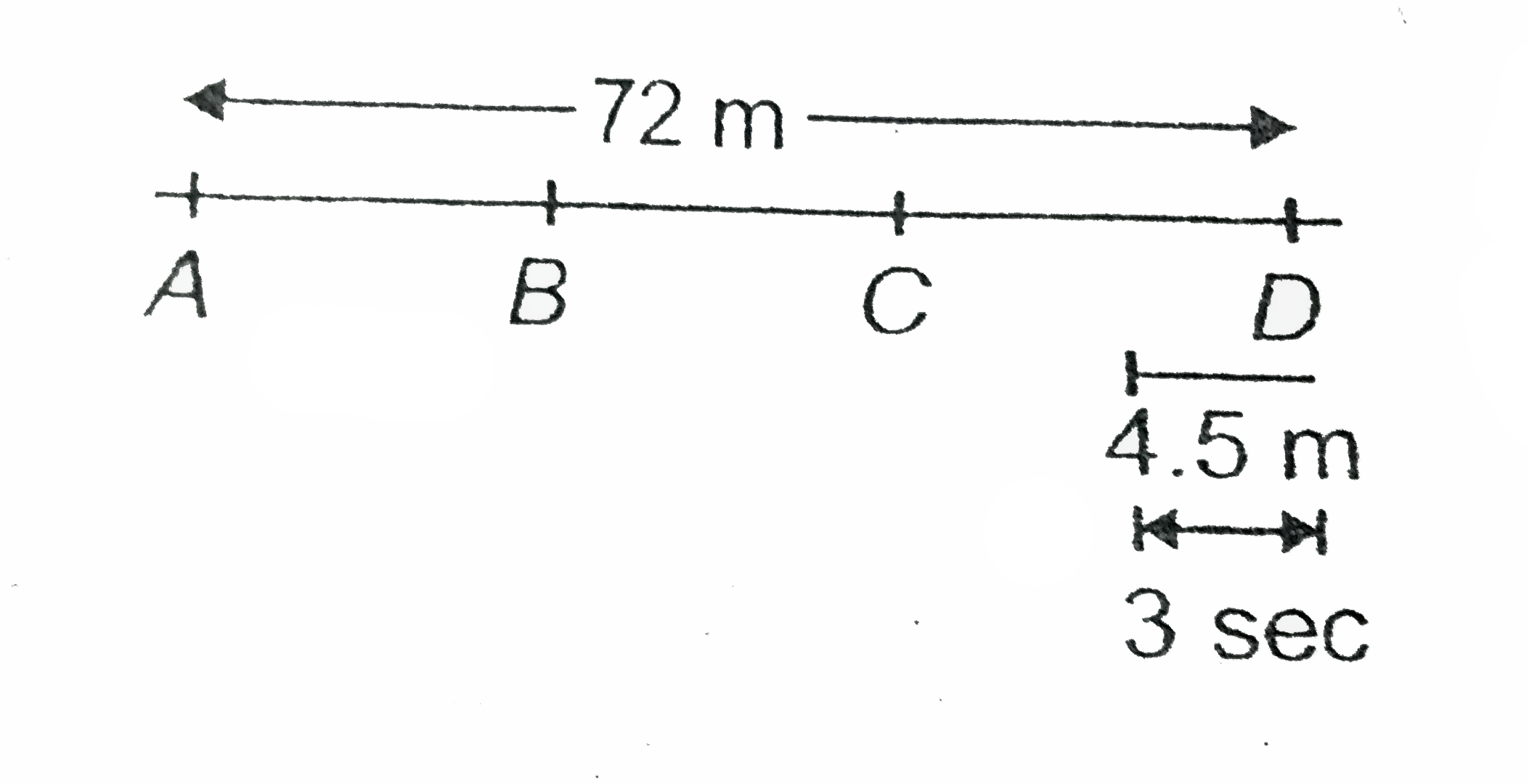
The answer will be ''Yes'' if the particle moves without reversing its direction of motion in the specified interval but the answer will be ''No'' if the particle reverses its direction of motion in the specified interval of time.
In the present problem, in the interval of 15 s the particle reverses its direction of motion at t = 12 s.
Here, first find the distance travelled in 12 s and then the distance travelled in subsequent 3 s, then add them up. We have already found AD = 72 m. Now for the subsequent 3 s interval,
`u=0, a=-1m//s^(2),t=3s`
Distance `=|s|=|0xx3+(1)/(2)xx(-1)xx3^(2)|=4.5m`
`rArr" Distance covered in 15 s "=72+4.5=76.5m`