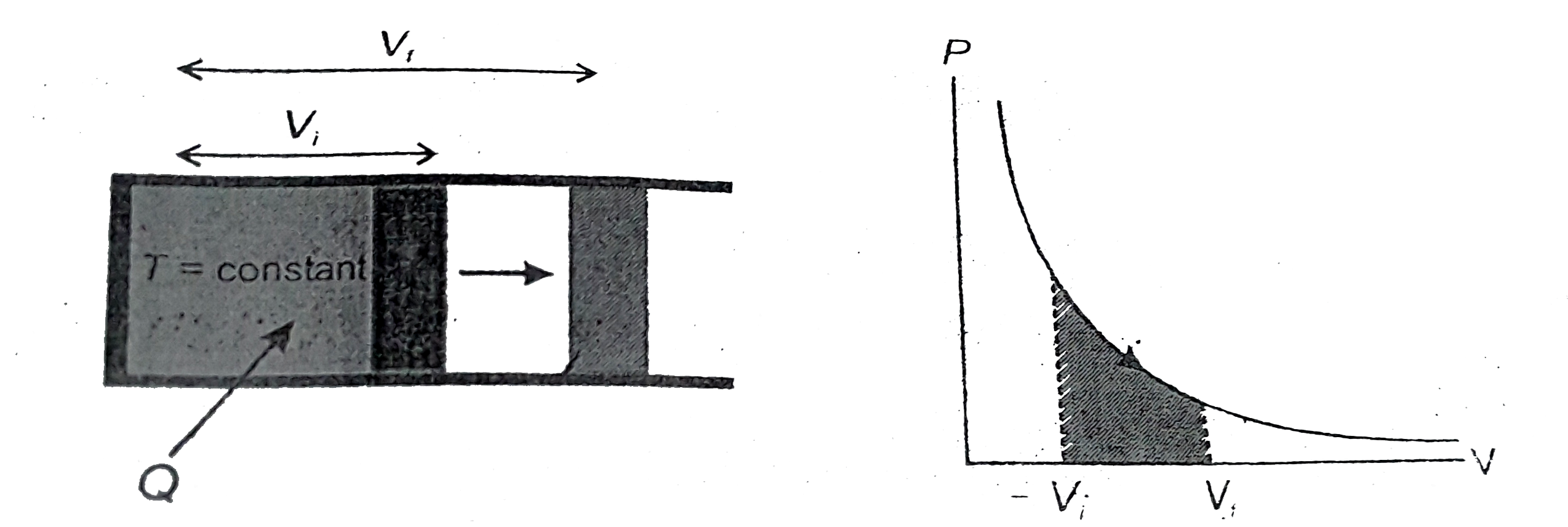
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A cylinder contains 0.50 mol of an ideal gas at temperature of 310 K. ...
Text Solution
|
- A gas is found to be obeyed the law p^2V = constant . The initial temp...
Text Solution
|
- A cyclinder contains 0.5 mole of an ideal gas at 310K . As the gas exp...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal gas expands at a constant temperature of 300 K fr...
Text Solution
|
- During an experiment an ideal gas is found to be obey an additional la...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder contains 0.50 mol of an ideal gas at temperature of 310 K. ...
Text Solution
|
- एक आदर्श गैस का ताप 300 K है, रुद्धोष्म प्रसार द्वारा इसका आयतन प्रारम...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature of an ideal gas is 340 K. the gas is heated to a tempe...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas at initial temperature T0 and initial volume V0 is expa...
Text Solution
|