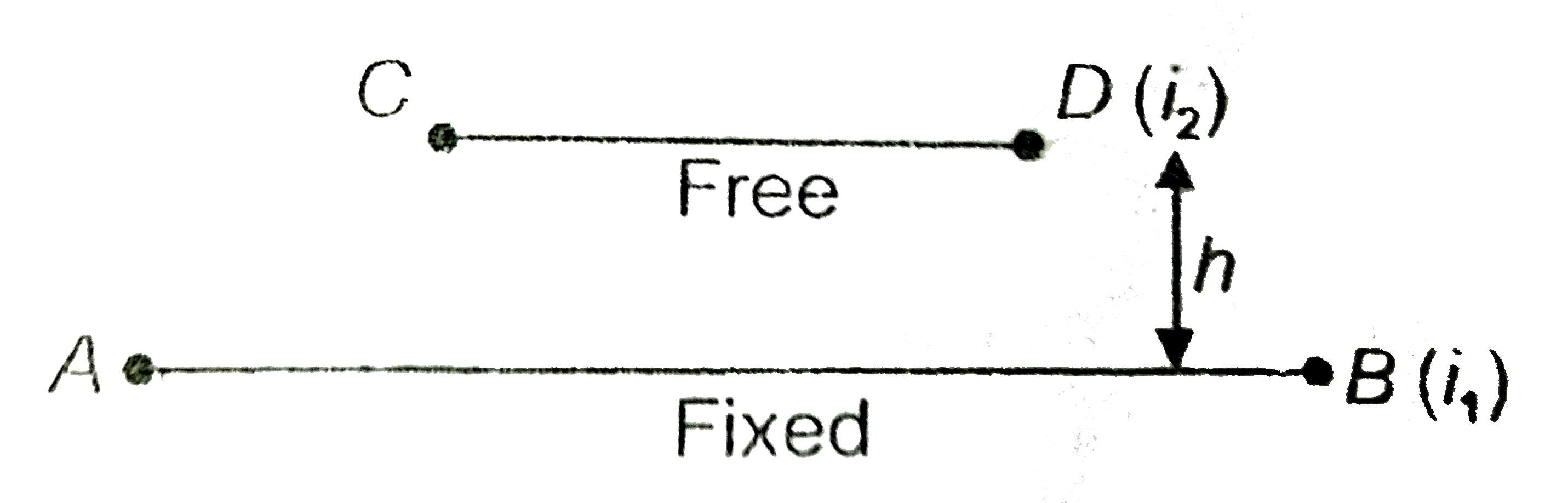
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
MOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise Assignment Section E (Assertion - Reason Type Questions)|8 VideosMOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise Assignment Section F (Matrix-Match Type Questions|4 VideosMOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise Assignment Section C (Objective Type Questions (More than one option are correct)|14 VideosMOVING CHARGE AND MAGNESIUM
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise SECTION D|16 VideosNUCLEI
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise ASSIGNMENT (SECTION-D)|10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH INSTITUTE-MOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM-Assignment Section D (Linked Comprehension Type Questions)
- The cyclotron is a device which is used to accelerate charged particle...
Text Solution
|
- The cyclotron is a device which is used to accelerate charged particle...
Text Solution
|
- The cyclotron is a device which is used to accelerate charged particle...
Text Solution
|
- A moving coil galvanometer consists of a coil of N turns are area A su...
Text Solution
|
- A moving coil galvanometer consists of a coil of N turns are area A su...
Text Solution
|
- A moving coil galvanometer consists of a coil of N turns are area A su...
Text Solution
|
- A moving coil galvanometer consists of a coil of N turns are area A su...
Text Solution
|
- The force per unit length between two parallel current carrying wires ...
Text Solution
|
- The force per unit length between two parallel current carrying wires ...
Text Solution
|