Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise Assignment (Section - A) Objective Type Questions (One option is correct)|38 VideosRAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise Assignment (Section - B) Objective Type Questions (One option is correct)|16 VideosPHYSICAL WORLD
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise ASSIGNMENT (Section-B)|5 VideosSEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS (MATERIAL, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRUITS )
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise Assignment SECTION - D (Assertion & reason type Question)|10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH INSTITUTE-RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS-ASSIGNMENT (SECTION - D)
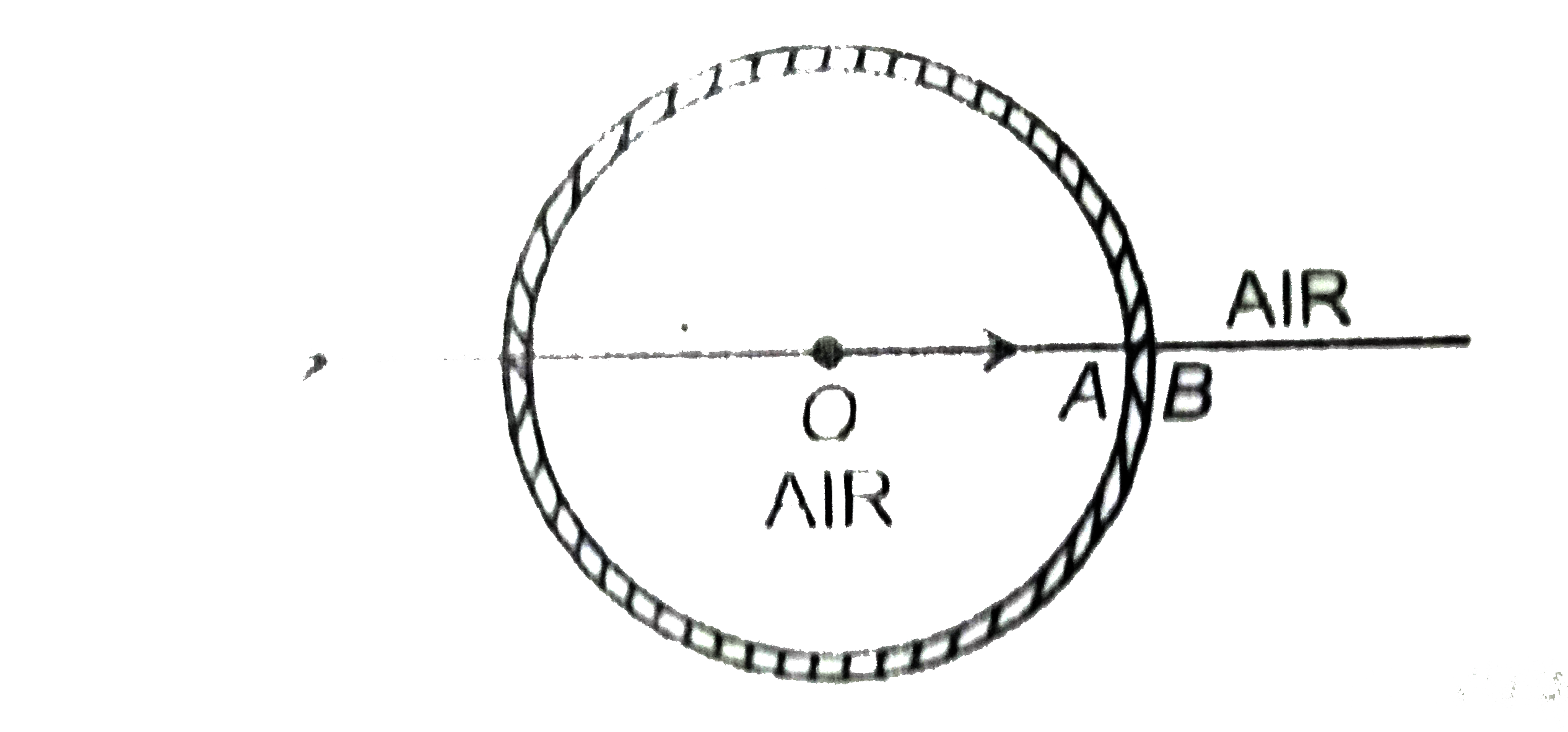
- A small filament is at the centre of a hollow glass sphere of inner an...
Text Solution
|
- A : Plane and convex mirrors can produce real images of objects. R :...
Text Solution
|
- A : A virtual image cannot be caught on a screen but it can be photogr...
Text Solution
|
- A : When a diver under water looks obliquely at a fisherman standing o...
Text Solution
|
- A : The apparent depth of a tank of water decreases if viewed obliquel...
Text Solution
|
- A : Proper cutting of diamond makes it sparkle. R : Diamond has very...
Text Solution
|
- A : The angle subtended at the eye by an object is equal to the angle ...
Text Solution
|
- A : In viewing through a magnifying glass, angular magnification decre...
Text Solution
|
- A : Magnifying power of a simple microscope cannot be increased beyond...
Text Solution
|
- A : The objective and the eye-piece of a compound microscope should ha...
Text Solution
|
- A : When viewing through a compound microscope, our eyes should be pos...
Text Solution
|
- A : The peculiar fish Anableps anableps swims with its eyes partially ...
Text Solution
|
- A : A virtual image cannot be produced on screen. R : The light ener...
Text Solution
|
- A : Lenses of large aperture suffer from spherical aberration. R : T...
Text Solution
|
- A : The image formed by a concave lens is always virtual. R : The ra...
Text Solution
|
- A : When two lenses in contact form an achromatic doublet, then the ma...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : A reflecting type telescope is preferred over refracting t...
Text Solution
|